ERK and JNK activation is essential for oncogenic transformation by v-Rel
- PMID: 20802521
- PMCID: PMC2992084
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.359
ERK and JNK activation is essential for oncogenic transformation by v-Rel
Abstract
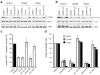
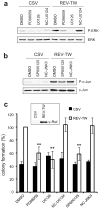
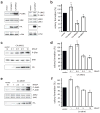
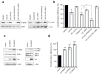
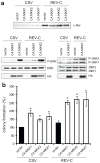
v-Rel is the acutely oncogenic member of the NF-κB family of transcription factors. Infection with retroviruses expressing v-Rel rapidly induces fatal lymphomas in birds and transforms primary lymphocytes and fibroblasts in vitro. We have previously shown that AP-1 transcriptional activity contributes to v-Rel-mediated transformation. Although v-Rel increases the expression of these factors, their activity may also be induced through phosphorylation by the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs). The expression of v-Rel results in the strong and sustained activation of the ERK and JNK MAPK pathways. This induction is critical for the v-Rel-transformed phenotype, as suppression of MAPK activity with chemical inhibitors or small interfering RNA severely impairs colony formation of v-Rel-transformed lymphoid cell lines. However, signaling must be maintained within an optimal range in these cells, as strong additional activation of either pathway beyond the levels induced by v-Rel through the expression of constitutively active MAPK proteins attenuates the transformed phenotype. MAPK signaling also has an important role in the initial transformation of primary spleen cells by v-Rel, although distinct requirements for MAPK activity at different stages of v-Rel-mediated transformation were identified. We also show that the ability of v-Rel to induce MAPK signaling more strongly than c-Rel contributes to its greater oncogenicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

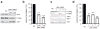
References
-
- Basseres DS, Baldwin AS. Nuclear factor- B and inhibitor of B kinase pathways in oncogenic initiation and progression. Oncogene. 2006;25:6817–30. - PubMed
-
- Blume-Jensen P, Hunter T. Oncogenic kinase signalling. Nature. 2001;411:355–65. - PubMed
-
- Bonizzi G, Karin M. The two NF- B activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol. 2004;25:280–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

