CpG island hypermethylation-associated silencing of non-coding RNAs transcribed from ultraconserved regions in human cancer
- PMID: 20802525
- PMCID: PMC3007676
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.361
CpG island hypermethylation-associated silencing of non-coding RNAs transcribed from ultraconserved regions in human cancer
Erratum in
-
Correction: CpG island hypermethylation-associated silencing of non-coding RNAs transcribed from ultraconserved regions in human cancer.Oncogene. 2019 Jan;38(5):765-766. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0560-1. Oncogene. 2019. PMID: 30397238 Free PMC article.
Abstract
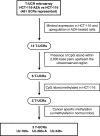
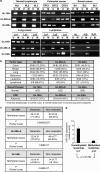
Although only 1.5% of the human genome appears to code for proteins, much effort in cancer research has been devoted to this minimal fraction of our DNA. However, the last few years have witnessed the realization that a large class of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), named microRNAs, contribute to cancer development and progression by acting as oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes. Recent studies have also shown that epigenetic silencing of microRNAs with tumor suppressor features by CpG island hypermethylation is a common hallmark of human tumors. Thus, we wondered whether there were other ncRNAs undergoing aberrant DNA methylation-associated silencing in transformed cells. We focused on the transcribed-ultraconserved regions (T-UCRs), a subset of DNA sequences that are absolutely conserved between orthologous regions of the human, rat and mouse genomes and that are located in both intra- and intergenic regions. We used a pharmacological and genomic approach to reveal the possible existence of an aberrant epigenetic silencing pattern of T-UCRs by treating cancer cells with a DNA-demethylating agent followed by hybridization to an expression microarray containing these sequences. We observed that DNA hypomethylation induces release of T-UCR silencing in cancer cells. Among the T-UCRs that were reactivated upon drug treatment, Uc.160+, Uc283+A and Uc.346+ were found to undergo specific CpG island hypermethylation-associated silencing in cancer cells compared with normal tissues. The analysis of a large set of primary human tumors (n=283) demonstrated that hypermethylation of the described T-UCR CpG islands was a common event among the various tumor types. Our finding that, in addition to microRNAs, another class of ncRNAs (T-UCRs) undergoes DNA methylation-associated inactivation in transformed cells supports a model in which epigenetic and genetic alterations in coding and non-coding sequences cooperate in human tumorigenesis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
CpG island hypermethylation-associated silencing of small nucleolar RNAs in human cancer.RNA Biol. 2012 Jun;9(6):881-90. doi: 10.4161/rna.19353. Epub 2012 May 23. RNA Biol. 2012. PMID: 22617881 Free PMC article.
-
The role of a new class of long noncoding RNAs transcribed from ultraconserved regions in cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2017 Dec;1868(2):449-455. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2017.09.001. Epub 2017 Sep 13. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28916343 Review.
-
A microRNA DNA methylation signature for human cancer metastasis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Sep 9;105(36):13556-61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803055105. Epub 2008 Sep 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18768788 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant methylation and silencing of ARHI, an imprinted tumor suppressor gene in which the function is lost in breast cancers.Cancer Res. 2003 Jul 15;63(14):4174-80. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12874023
-
The dark matter of the human genome and its role in human cancers.Gene. 2022 Feb 15;811:146084. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2021.146084. Epub 2021 Nov 26. Gene. 2022. PMID: 34843880 Review.
Cited by
-
Secondary structure impacts patterns of selection in human lncRNAs.BMC Biol. 2016 Jul 25;14:60. doi: 10.1186/s12915-016-0283-0. BMC Biol. 2016. PMID: 27457204 Free PMC article.
-
Globally increased ultraconserved noncoding RNA expression in pancreatic adenocarcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 16;7(33):53165-53177. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10242. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27363020 Free PMC article.
-
LINC00543 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by driving EMT and inducing the M2 polarization of tumor associated macrophages.J Transl Med. 2023 Feb 25;21(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04009-6. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36841801 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the role of long non-coding RNAs in DNA methylation mediated transcriptional regulation.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Dec 2;9:1067406. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1067406. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36533073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging role of lncRNAs in the regulation of cancer stem cells.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018 Dec;41(6):585-603. doi: 10.1007/s13402-018-0406-4. Epub 2018 Sep 14. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018. PMID: 30218296 Review.
References
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Bejerano G, Lowe CB, Ahituv N, King B, Siepel A, Salama SR, et al. A distal enhancer and an ultraconserved exon are derived from a novel retroposon. Nature. 2006;441:87–90. - PubMed
-
- Bejerano G, Pheasant M, Makunin I, Stephen S, Kent WJ, Mattick JS, et al. Ultraconserved elements in the human genome. Science. 2004;304:1321–1325. - PubMed

