The combination of rifampin plus moxifloxacin is synergistic for suppression of resistance but antagonistic for cell kill of Mycobacterium tuberculosis as determined in a hollow-fiber infection model
- PMID: 20802826
- PMCID: PMC2925073
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00139-10
The combination of rifampin plus moxifloxacin is synergistic for suppression of resistance but antagonistic for cell kill of Mycobacterium tuberculosis as determined in a hollow-fiber infection model
Abstract
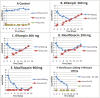
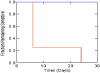
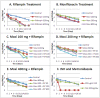
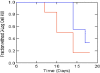
Moxifloxacin is under development for expanded use against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Rifampin is a mainstay of therapy. We examined the interaction of moxifloxacin plus rifampin for log-phase and nonreplicating persister (NRP) organisms. For this evaluation, we employed our hollow-fiber infection model, in which organisms are exposed to clinically relevant drug concentration-time profiles and the impact on bacterial cell kill and resistant subpopulation amplification is determined. In log phase, resistance emergence was observed in all monotherapy regimens and in no combination therapy regimen. No difference was seen in time to a 3-log reduction in the bacterial burden; there was a significant difference in time to resistance emergence (P = 0.0006). In the NRP experiment, no resistance emergence was seen. There was a significant difference between the monotherapy and combination therapy regimens in time to a 3-log reduction in the bacterial burden (P = 0.042). The combination is efficacious for suppressing resistant organisms but is antagonistic for cell kill.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of administration of moxifloxacin plus rifampin against Mycobacterium tuberculosis for 7 of 7 days versus 5 of 7 days in an in vitro pharmacodynamic system.mBio. 2011 Jul 12;2(4):e00108-11. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00108-11. Print 2011. mBio. 2011. PMID: 21750119 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro postantibiotic effects of rifapentine, isoniazid, and moxifloxacin against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 Jan;48(1):340-3. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.1.340-343.2004. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004. PMID: 14693563 Free PMC article.
-
Activity of Moxifloxacin against Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Acid Phase and Nonreplicative-Persister Phenotype Phase in a Hollow-Fiber Infection Model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Nov 26;62(12):e01470-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01470-18. Print 2018 Dec. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 30249693 Free PMC article.
-
New antituberculous drugs in development.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2010 Aug;7(3):143-51. doi: 10.1007/s11904-010-0054-4. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2010. PMID: 20559756 Review.
-
Targeting Phenotypically Tolerant Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Microbiol Spectr. 2017 Jan;5(1):10.1128/microbiolspec.tbtb2-0031-2016. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.TBTB2-0031-2016. Microbiol Spectr. 2017. PMID: 28233509 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PK/PD models in antibacterial development.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2013 Oct;16(5):573-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2013.06.010. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23871724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cumulative Fraction of Response for Once- and Twice-Daily Delamanid in Patients with Pulmonary Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Dec 16;65(1):e01207-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01207-20. Print 2020 Dec 16. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 33106263 Free PMC article.
-
Tuberculosis drugs' distribution and emergence of resistance in patient's lung lesions: A mechanistic model and tool for regimen and dose optimization.PLoS Med. 2019 Apr 2;16(4):e1002773. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002773. eCollection 2019 Apr. PLoS Med. 2019. PMID: 30939136 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of spectinamide 1599 efficacy against different mycobacterial phenotypes.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2023 May;140:102342. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2023.102342. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2023. PMID: 37120915 Free PMC article.
-
A rifapentine-containing inhaled triple antibiotic formulation for rapid treatment of tubercular infection.Pharm Res. 2014 May;31(5):1239-53. doi: 10.1007/s11095-013-1245-7. Epub 2013 Nov 16. Pharm Res. 2014. PMID: 24242939
References
-
- Dickinson J. M., Aber V. R., Mitchison D. A. 1977. Bactericidal activity of streptomycin, isoniazid, rifampin, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide alone and in combination against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 116:637–635 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

