Optical mapping of release properties in synapses
- PMID: 20802854
- PMCID: PMC2928663
- DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2010.00018
Optical mapping of release properties in synapses
Abstract
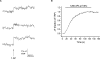
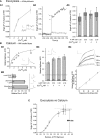
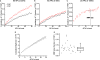
Synapses are important functional units that determine how information flows through the brain. Understanding their biophysical properties and the molecules that underpin them is an important goal of cellular neuroscience. Thus, it is of interest to develop protocols that allow easy measurement of synaptic parameters in model systems that permit molecular manipulations. Here, we used a sensitive and high-time resolution optical approach that allowed us to characterize two functional parameters critical to presynaptic efficacy: vesicle fusion probability (Pv) and readily-releasable pool size (RRP). We implemented two different approaches to determine the RRP size that were in broad agreement: depletion of the RRP by high-frequency stimulation and saturation of the calcium sensor during single action potential stimuli. Our methods are based on reporters that provide a robust, quantitative, purely presynaptic readout and present a new avenue to study molecules that affect synaptic vesicle exocytosis.
Keywords: exocytosis; imaging; pHluorin; readily-releasable pool; release probability; synapse.
Figures
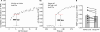
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

