The diagnostic value of CRP, IL-8, PCT, and sTREM-1 in the detection of bacterial infections in pediatric oncology patients with febrile neutropenia
- PMID: 20803037
- PMCID: PMC3166608
- DOI: 10.1007/s00520-010-0987-6
The diagnostic value of CRP, IL-8, PCT, and sTREM-1 in the detection of bacterial infections in pediatric oncology patients with febrile neutropenia
Abstract
Purpose: In this study, we evaluated C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin (IL)-8, procalcitonin (PCT), and soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 (sTREM-1) as predictors for bacterial infection in febrile neutropenia, plus their usefulness in febrile neutropenia during chemotherapy-induced gastrointestinal mucositis.
Methods: Plasma was obtained from pediatric oncology patients at presentation with febrile neutropenia (n = 43) and 24-48 h later (n = 17). The patients were classified as having or not having a bacterial infection. Plasma was also obtained of patients in the absence and in the presence of mucositis (n = 26).
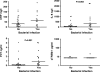
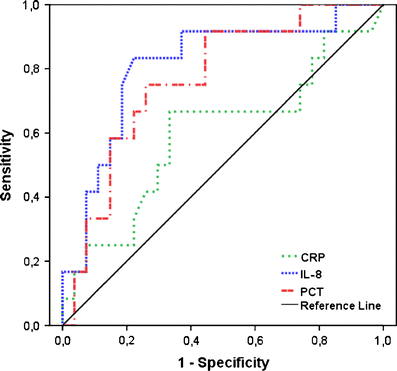
Results: At presentation with febrile neutropenia, median IL-8 and PCT levels were significantly increased in patients with a bacterial infection, in contrast to CRP and sTREM-1. IL-8 was the most sensitive marker for the early detection of bacterial infection, in combination with clinical parameters or PCT the sensitivity reached 100%. After 24-48 h, only PCT was significantly elevated during bacterial infection. IL-8 levels were significantly increased during mucositis. Mucositis did not cause considerable changes in PCT levels.
Conclusions: IL-8 is the most useful marker for the early detection of bacterial infections, compared with CRP, PCT, and sTREM-1. IL-8 in combination with clinical parameters or PCT might be even more useful. Gastrointestinal mucositis alone does not affect PCT levels, in contrast to IL-8 levels, and therefore, PCT might be more useful for the detection of bacterial infections during mucositis than IL-8.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diagnostic value of sTREM-1, IL-8, PCT, and CRP in febrile neutropenia after autologous stem cell transplantation.Ann Hematol. 2017 Dec;96(12):2095-2101. doi: 10.1007/s00277-017-3128-1. Epub 2017 Sep 17. Ann Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28920169 Clinical Trial.
-
Prospective Evaluation of Procalcitonin, Soluble Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells-1 and C-Reactive Protein in Febrile Patients with Autoimmune Diseases.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 20;11(4):e0153938. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153938. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27096761 Free PMC article.
-
Procalcitonin in paediatric cancer patients: its diagnostic relevance is superior to that of C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, interleukin 8, soluble interleukin 2 receptor and soluble tumour necrosis factor receptor II.Br J Haematol. 2000 Dec;111(4):1093-102. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2000.02458.x. Br J Haematol. 2000. PMID: 11167745
-
PCT and sTREM-1: the markers of infection in critically ill patients?Med Sci Monit. 2008 Dec;14(12):RA241-7. Med Sci Monit. 2008. PMID: 19043381 Review.
-
The role of procalcitonin in febrile neutropenic patients: review of the literature.Infection. 2008 Oct;36(5):396-407. doi: 10.1007/s15010-008-7374-y. Epub 2008 Aug 30. Infection. 2008. PMID: 18759057 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune regulation of procalcitonin: a biomarker and mediator of infection.Inflamm Res. 2012 May;61(5):401-9. doi: 10.1007/s00011-012-0439-5. Epub 2012 Feb 22. Inflamm Res. 2012. PMID: 22354317 Review.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic value of procalcitonin for early intracranial infection after craniotomy.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2017 Apr 20;50(5):e6021. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20176021. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2017. PMID: 28443989 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-inflammatory cytokine ratios determine the clinical course of febrile neutropenia in children receiving chemotherapy.Mol Cell Pediatr. 2020 Jun 9;7(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s40348-020-00097-2. Mol Cell Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32519027 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers and non-invasive tests for gastrointestinal mucositis.Support Care Cancer. 2017 Sep;25(9):2933-2941. doi: 10.1007/s00520-017-3752-2. Epub 2017 May 24. Support Care Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28536886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retrospective analysis of cancer patients admitted to a tertiary centre with suspected neutropenic sepsis: Are C-reactive protein and neutrophil count useful prognostic biomarkers?J Intensive Care Soc. 2018 May;19(2):132-137. doi: 10.1177/1751143717741248. Epub 2017 Dec 4. J Intensive Care Soc. 2018. PMID: 29796070 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bodey GP, Buckley M, Sathe YS, Freireich EJ. Quantitative relationships between circulating leukocytes and infection in patients with acute leukemia. Ann Intern Med. 1966;64:328–340. - PubMed
-
- Hann I, Viscoli C, Paesmans M, Gaya H, Glauser M. A comparison of outcome from febrile neutropenic episodes in children compared with adults: results from four EORTC studies. International Antimicrobial Therapy Cooperative Group (IATCG) of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Br J Haematol. 1997;99:580–588. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.1997.4453255.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

