p53 and p21(Waf1) are recruited to distinct PML-containing nuclear foci in irradiated and Nutlin-3a-treated U2OS cells
- PMID: 20803550
- PMCID: PMC3613244
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.22852
p53 and p21(Waf1) are recruited to distinct PML-containing nuclear foci in irradiated and Nutlin-3a-treated U2OS cells
Abstract
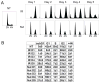
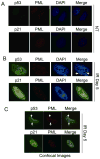
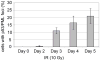
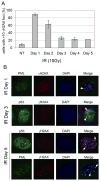
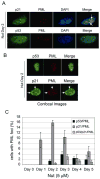
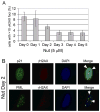
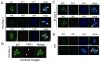
Promyelocytic leukemia nuclear bodies (PML-NBs) are multiprotein complexes that include PML protein and localize in nuclear foci. PML-NBs are implicated in multiple stress responses, including apoptosis, DNA repair, and p53-dependent growth inhibition. ALT-associated PML bodies (APBs) are specialized PML-NBs that include telomere-repeat binding-factor TRF1 and are exclusively in telomerase-negative tumors where telomere length is maintained through alternative (ALT) recombination mechanisms. We compared cell-cycle and p53 responses in ALT-positive cancer cells (U2OS) exposed to ionizing radiation (IR) or the p53 stabilizer Nutlin-3a. Both IR and Nutlin-3a caused growth arrest and comparable induction of p53. However, p21, whose gene p53 activates, displayed biphasic induction following IR and monophasic induction following Nutlin-3a. p53 was recruited to PML-NBs 3-4 days after IR, approximately coincident with the secondary p21 increase. These p53/PML-NBs marked sites of apparently unrepaired DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), identified by colocalization with phosphorylated histone H2AX. Both Nutlin-3a and IR caused a large increase in APBs that was dependent on p53 and p21 expression. Moreover, p21, and to a lesser extent p53, was recruited to APBs in a fraction of Nutlin-3a-treated cells. These data indicate (1) p53 is recruited to PML-NBs after IR that likely mark unrepaired DSBs, suggesting p53 may either be further activated at these sites and/or function in their repair; (2) p53-p21 pathway activation increases the percentage of APB-positive cells, (3) p21 and p53 are recruited to ALT-associated PML-NBs after Nutlin-3a treatment, suggesting that they may play a previously unrecognized role in telomere maintenance.
Copyright © 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

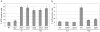
Similar articles
-
HDM2 antagonist Nutlin-3 disrupts p73-HDM2 binding and enhances p73 function.Oncogene. 2008 Feb 7;27(7):997-1003. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210707. Epub 2007 Aug 13. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 17700533
-
Knocking down PML impairs p53 signaling transduction pathway and suppresses irradiation induced apoptosis in breast carcinoma cell MCF-7.J Cell Biochem. 2006 Feb 15;97(3):561-71. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20584. J Cell Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16215989
-
Induction of alternative lengthening of telomeres-associated PML bodies by p53/p21 requires HP1 proteins.J Cell Biol. 2009 Jun 1;185(5):797-810. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200810084. Epub 2009 May 25. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19468068 Free PMC article.
-
Role of nuclear bodies in apoptosis signalling.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Nov;1783(11):2185-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.07.002. Epub 2008 Jul 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18680765 Review.
-
The functional roles of PML nuclear bodies in genome maintenance.Mutat Res. 2018 May;809:99-107. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2017.05.002. Epub 2017 May 5. Mutat Res. 2018. PMID: 28521962 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Annexin 7 (ANXA7) as a Tumor Suppressor and a Regulator of Drug Resistance in Thyroid Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 9;25(23):13217. doi: 10.3390/ijms252313217. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684934 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 regulates inflammatory response to stress.Inflamm Res. 2012 Dec;61(12):1395-404. doi: 10.1007/s00011-012-0542-7. Epub 2012 Aug 17. Inflamm Res. 2012. PMID: 22899279 Free PMC article.
-
Retrotransposon-derived p53 binding sites enhance telomere maintenance and genome protection.Bioessays. 2016 Oct;38(10):943-9. doi: 10.1002/bies.201600078. Epub 2016 Aug 19. Bioessays. 2016. PMID: 27539745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CYP2E1 in 1,4-dioxane metabolism and liver toxicity: insights from CYP2E1 knockout mice study.Arch Toxicol. 2024 Oct;98(10):3241-3257. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03811-5. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Arch Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39192018
-
p21-activated kinase 7 is an oncogene in human osteosarcoma.Cell Biol Int. 2014 Dec;38(12):1394-402. doi: 10.1002/cbin.10351. Epub 2014 Aug 6. Cell Biol Int. 2014. PMID: 25052921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bernardi R, Pandolfi PP. Structure, dynamics and functions of promyelocytic leukaemia nuclear bodies. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:1006–16. - PubMed
-
- Boehme KA, Blattner C. Regulation of p53--insights into a complex process. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2009;44:367–92. - PubMed
-
- Brown L, Boswell S, Raj L, Lee SW. Transcriptional targets of p53 that regulate cellular proliferation. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2007;17:73–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

