Small-molecule regulators that mimic transcription factors
- PMID: 20804876
- PMCID: PMC4160733
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.08.010
Small-molecule regulators that mimic transcription factors
Abstract
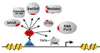
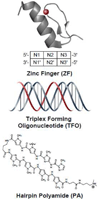
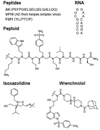
Transcription factors (TFs) are responsible for decoding and expressing the information stored in the genome, which dictates cellular function. Creating artificial transcription factors (ATFs) that mimic endogenous TFs is a major goal at the interface of biology, chemistry, and molecular medicine. Such molecular tools will be essential for deciphering and manipulating transcriptional networks that lead to particular cellular states. In this minireview, the framework for the design of functional ATFs is presented and current challenges in the successful implementation of ATFs are discussed.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
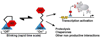
Similar articles
-
From Peptides to Peptidomimetics: A Strategy Based on the Structural Features of Cyclopropane.Chemistry. 2017 Oct 17;23(58):14394-14409. doi: 10.1002/chem.201702119. Epub 2017 Aug 22. Chemistry. 2017. PMID: 28632330 Review.
-
The new biomimetic chemistry: artificial transcription factors.ACS Chem Biol. 2007 Sep 21;2(9):599-601. doi: 10.1021/cb700183s. ACS Chem Biol. 2007. PMID: 17894442 Review.
-
Reprogramming cell fate with a genome-scale library of artificial transcription factors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Dec 20;113(51):E8257-E8266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1611142114. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27930301 Free PMC article.
-
Recent development of small antimicrobial peptidomimetics.Future Med Chem. 2012 Sep;4(14):1853-62. doi: 10.4155/fmc.12.111. Future Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 23043481 Review.
-
Peptidomimetic toolbox for drug discovery.Chem Soc Rev. 2020 Jun 7;49(11):3262-3277. doi: 10.1039/d0cs00102c. Epub 2020 Apr 7. Chem Soc Rev. 2020. PMID: 32255135 Review.
Cited by
-
Controlling gene networks and cell fate with precision-targeted DNA-binding proteins and small-molecule-based genome readers.Biochem J. 2014 Sep 15;462(3):397-413. doi: 10.1042/BJ20140400. Biochem J. 2014. PMID: 25145439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Concise review: Cancer cell reprogramming and therapeutic implications.Transl Oncol. 2022 Oct;24:101503. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2022.101503. Epub 2022 Aug 4. Transl Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35933935 Free PMC article.
-
Improving motor neuron-like cell differentiation of hEnSCs by the combination of epothilone B loaded PCL microspheres in optimized 3D collagen hydrogel.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 5;11(1):21722. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01071-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34741076 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescent probes for nucleic Acid visualization in fixed and live cells.Molecules. 2013 Dec 11;18(12):15357-97. doi: 10.3390/molecules181215357. Molecules. 2013. PMID: 24335616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrating epigenetic modulators into NanoScript for enhanced chondrogenesis of stem cells.J Am Chem Soc. 2015 Apr 15;137(14):4598-601. doi: 10.1021/ja511298n. Epub 2015 Apr 2. J Am Chem Soc. 2015. PMID: 25789886 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hauschild KE, Carlson CD, Donato LJ, Moretti R, Ansari AZ. Transcription Factors. In: Begley T, editor. Wiley Encyclopedia of Chemical Biology. Vol. 4. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 2008. pp. 566–584.
-
- Darnell JE. Transcription factors as targets for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2002;2:740–749. - PubMed
-
- Brennan P, Donev R, Hewamana S. Targeting transcription factors for therapeutic benefit. Mol. Biosys. 2008;4:909–919. - PubMed
-
- Arora PS, Ansari AZ. A Notch above other inhibitors. Nature. 2009;462:171–173. - PubMed
-
- Ptashne M, Gann A. Genes and Signals. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Press; 2002.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

