Functional diversity of ESC-derived motor neuron subtypes revealed through intraspinal transplantation
- PMID: 20804971
- PMCID: PMC2933095
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2010.07.013
Functional diversity of ESC-derived motor neuron subtypes revealed through intraspinal transplantation
Abstract
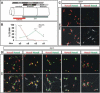
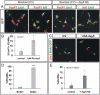
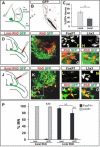
Cultured ESCs can form different classes of neurons, but whether these neurons can acquire specialized subtype features typical of neurons in vivo remains unclear. We show here that mouse ESCs can be directed to form highly specific motor neuron subtypes in the absence of added factors, through a differentiation program that relies on endogenous Wnts, FGFs, and Hh-mimicking the normal program of motor neuron subtype differentiation. Molecular markers that characterize motor neuron subtypes anticipate the functional properties of these neurons in vivo: ESC-derived motor neurons grafted isochronically into chick spinal cord settle in appropriate columnar domains and select axonal trajectories with a fidelity that matches that of their in vivo generated counterparts. ESC-derived motor neurons can therefore be programmed in a predictive manner to acquire molecular and functional properties that characterize one of the many dozens of specialized motor neuron subtypes that exist in vivo.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Subtype Diversification and Synaptic Specificity of Stem Cell-Derived Spinal Interneurons.Neuron. 2018 Oct 10;100(1):135-149.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.09.016. Neuron. 2018. PMID: 30308166 Free PMC article.
-
Xenotransplantation of embryonic stem cell-derived motor neurons into the developing chick spinal cord.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;482:171-83. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-060-7_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19089356
-
Cytochrome p450 cyp26a1 alters spinal motor neuron subtype identity in differentiating embryonic stem cells.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 4;288(40):28801-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.474254. Epub 2013 Aug 13. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23946489 Free PMC article.
-
Programming embryonic stem cells to neuronal subtypes.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2011 Feb;21(1):43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2010.09.012. Epub 2010 Oct 20. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 20970319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Motor neuron derivation from human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells: experimental approaches and clinical perspectives.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014 Jul 14;5(4):87. doi: 10.1186/scrt476. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25157556 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endogenous neural stem cells in central canal of adult rats acquired limited ability to differentiate into neurons following mild spinal cord injury.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Apr 1;8(4):3835-42. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26097566 Free PMC article.
-
Neural Conversion and Patterning of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells: A Developmental Perspective.Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:8291260. doi: 10.1155/2016/8291260. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Stem Cells Int. 2016. PMID: 27069483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An optogenetic cell therapy to restore control of target muscles in an aggressive mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Elife. 2024 Jan 18;12:RP88250. doi: 10.7554/eLife.88250. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38236205 Free PMC article.
-
Subtype Diversification and Synaptic Specificity of Stem Cell-Derived Spinal Interneurons.Neuron. 2018 Oct 10;100(1):135-149.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.09.016. Neuron. 2018. PMID: 30308166 Free PMC article.
-
Fully Characterized Mature Human iPS- and NMP-Derived Motor Neurons Thrive Without Neuroprotection in the Spinal Contusion Cavity.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Jan 3;15:725195. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.725195. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35046774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersson E, Tryggvason U, Deng Q, Friling S, Alekseenko Z, Robert B, Perlmann T, Ericson J. Identification of intrinsic determinants of midbrain dopamine neurons. Cell. 2006;124:393–405. - PubMed
-
- Arber S, Ladle DR, Lin JH, Frank E, Jessell TM. ETS gene Er81 controls the formation of functional connections between group Ia sensory afferents and motor neurons. Cell. 2000;101:485–498. - PubMed
-
- Bain G, Kitchens D, Yao M, Huettner JE, Gottlieb DI. Embryonic stem cells express neuronal properties in vitro. Dev Biol. 1995;168:342–357. - PubMed
-
- Buck L, Axel R. A novel multigene family may encode odorant receptors: A molecular basis for odor recognition. Cell. 1991;65:175–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

