Premature centromere division of metaphase chromosomes in peripheral blood lymphocytes of Alzheimer's disease patients: relation to gender and age
- PMID: 20805239
- PMCID: PMC2990265
- DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glq148
Premature centromere division of metaphase chromosomes in peripheral blood lymphocytes of Alzheimer's disease patients: relation to gender and age
Abstract
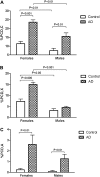
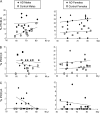
Chromosomal alterations are a feature of both aging and Alzheimer's disease (AD). This study examined if premature centromere division (PCD), a chromosomal instability indicator increased in AD, is correlated with aging or, instead, represents a de novo chromosomal alteration due to accelerating aging in AD. PCD in peripheral blood lymphocytes was determined in sporadic AD patients and gender and age-matched unaffected controls. Metaphase nuclei were analyzed for chromosomes showing PCD, X chromosomes with PCD (PCD,X), and acrocentric chromosomes showing PCD. AD patients, regardless of age, demonstrated increased PCD on any chromosome and PCD on acrocentric chromosomes in both genders, whereas an increase in frequency of PCD,X was expressed only in women. This cytogenetic analysis suggests that PCD is a feature of AD, rather than an epiphenomenon of chronological aging, and may be useful as a physiological biomarker that can be used for disease diagnosis.
Figures

References
-
- Smith MA. Alzheimer disease. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1998;42:1–54. - PubMed
-
- Zhu X, Castellani RJ, Takeda A, et al. Differential activation of neuronal ERK, JNK/SAPK and p38 in Alzheimer disease: the ‘two hit’ hypothesis. Mech Ageing Dev. 2001;123:39–46. - PubMed
-
- Zhu X, Lee HG, Perry G, Smith MA. Alzheimer disease, the two-hit hypothesis: an update. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1772:494–502. - PubMed
-
- Zhu X, Raina AK, Perry G, Smith MA. Alzheimer's disease: the two-hit hypothesis. Lancet Neurol. 2004;3:219–226. - PubMed
-
- Schellenberg GD. Early Alzheimer's disease genetics. J Alzheimers Dis. 2006;9:367–372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

