Extended Bayesian LASSO for multiple quantitative trait loci mapping and unobserved phenotype prediction
- PMID: 20805559
- PMCID: PMC2975286
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.110.119586
Extended Bayesian LASSO for multiple quantitative trait loci mapping and unobserved phenotype prediction
Abstract
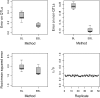
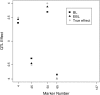
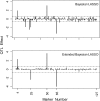
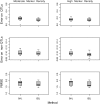
The Bayesian LASSO (BL) has been pointed out to be an effective approach to sparse model representation and successfully applied to quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping and genomic breeding value (GBV) estimation using genome-wide dense sets of markers. However, the BL relies on a single parameter known as the regularization parameter to simultaneously control the overall model sparsity and the shrinkage of individual covariate effects. This may be idealistic when dealing with a large number of predictors whose effect sizes may differ by orders of magnitude. Here we propose the extended Bayesian LASSO (EBL) for QTL mapping and unobserved phenotype prediction, which introduces an additional level to the hierarchical specification of the BL to explicitly separate out these two model features. Compared to the adaptiveness of the BL, the EBL is "doubly adaptive" and thus, more robust to tuning. In simulations, the EBL outperformed the BL in regard to the accuracy of both effect size estimates and phenotypic value predictions, with comparable computational time. Moreover, the EBL proved to be less sensitive to tuning than the related Bayesian adaptive LASSO (BAL), which introduces locus-specific regularization parameters as well, but involves no mechanism for distinguishing between model sparsity and parameter shrinkage. Consequently, the EBL seems to point to a new direction for QTL mapping, phenotype prediction, and GBV estimation.
Figures


References
-
- Gilks, W.R., S. Richardson and D. J. Spiegelhalter, 1996. Markov Chain Monte Carlo in Practice. Chapman & Hall, London.
-
- Hoerl, A. E., and R. W. Kennard, 1970. Ridge regression: biased estimation for nonorthogonal problems. Technometrics 12 55–67.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

