IL-10 inhibits transcription elongation of the human TNF gene in primary macrophages
- PMID: 20805562
- PMCID: PMC2947066
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20100414
IL-10 inhibits transcription elongation of the human TNF gene in primary macrophages
Abstract
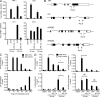
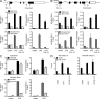
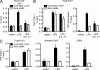
IL-10 plays a central nonredundant role in limiting inflammation in vivo. However, the mechanisms involved remain to be resolved. Using primary human macrophages, we found that IL-10 inhibits selected inflammatory genes, primarily at a level of transcription. At the TNF gene, this occurs not through an inhibition of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) recruitment and transcription initiation but through a mechanism targeting the stimulation of transcription elongation by cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 9. We demonstrated an unanticipated requirement for a region downstream of the TNF 3' untranslated region (UTR) that contains the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) binding motif (κB4) both for induction of transcription by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and its inhibition by IL-10. IL-10 not only inhibits the recruitment of RelA to regions containing κB sites at the TNF gene but also to those found at other LPS-induced genes. We show that although IL-10 elicits a general block in RelA recruitment to its genomic targets, the gene-specific nature of IL-10's actions are defined through the differential recruitment of CDK9 and the control of transcription elongation. At TNF, but not NFKBIA, the consequence of RelA recruitment inhibition is a loss of CDK9 recruitment, preventing the stimulation of transcription elongation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RelA Ser276 phosphorylation is required for activation of a subset of NF-kappaB-dependent genes by recruiting cyclin-dependent kinase 9/cyclin T1 complexes.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Jun;28(11):3623-38. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01152-07. Epub 2008 Mar 24. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18362169 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effect of chroman carboxamide on interleukin-6 expression in response to lipopolysaccharide by preventing nuclear factor-kappaB activation in macrophages.Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Aug 14;543(1-3):158-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.05.042. Epub 2006 Jun 2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16797005
-
MicroRNA-26b Modulates the NF-κB Pathway in Alveolar Macrophages by Regulating PTEN.J Immunol. 2015 Dec 1;195(11):5404-14. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402933. Epub 2015 Oct 26. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26503952 Free PMC article.
-
Nodakenin suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in macrophage cells by inhibiting tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 and nuclear factor-κB pathways and protects mice from lethal endotoxin shock.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Sep;342(3):654-64. doi: 10.1124/jpet.112.194613. Epub 2012 May 25. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012. PMID: 22637723
-
ATM regulates NF-κB-dependent immediate-early genes via RelA Ser 276 phosphorylation coupled to CDK9 promoter recruitment.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jul;42(13):8416-32. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku529. Epub 2014 Jun 23. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24957606 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
An extracellular matrix-mimetic coating with dual bionics for cardiovascular stents.Regen Biomater. 2023 May 30;10:rbad055. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbad055. eCollection 2023. Regen Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37359731 Free PMC article.
-
Perspective of cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (CDK9) as a drug target.Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(20):2883-90. doi: 10.2174/138161212800672750. Curr Pharm Des. 2012. PMID: 22571657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear factor of activated T cells is activated in the endothelium of retinal microvessels in diabetic mice.J Diabetes Res. 2015;2015:428473. doi: 10.1155/2015/428473. Epub 2015 Mar 31. J Diabetes Res. 2015. PMID: 25918731 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of titanium particle-induced inflammation by the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in murine macrophage-like RAW 264.7 cells.Inflammation. 2012 Aug;35(4):1411-8. doi: 10.1007/s10753-012-9454-5. Inflammation. 2012. PMID: 22427154
-
Decrease in IL-10 and increase in TNF-α levels in renal tissues during systemic inhibition of nitric oxide in anesthetized mice.Physiol Rep. 2014 Feb 10;2(2):e00228. doi: 10.1002/phy2.228. eCollection 2014 Feb 1. Physiol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24744897 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adelman K., Kennedy M.A., Nechaev S., Gilchrist D.A., Muse G.W., Chinenov Y., Rogatsky I. 2009. Immediate mediators of the inflammatory response are poised for gene activation through RNA polymerase II stalling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 106:18207–18212 10.1073/pnas.0910177106 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

