Autistic disorders and schizophrenia: related or remote? An anatomical likelihood estimation
- PMID: 20805880
- PMCID: PMC2923607
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012233
Autistic disorders and schizophrenia: related or remote? An anatomical likelihood estimation
Abstract
Shared genetic and environmental risk factors have been identified for autistic spectrum disorders (ASD) and schizophrenia. Social interaction, communication, emotion processing, sensorimotor gating and executive function are disrupted in both, stimulating debate about whether these are related conditions. Brain imaging studies constitute an informative and expanding resource to determine whether brain structural phenotype of these disorders is distinct or overlapping. We aimed to synthesize existing datasets characterizing ASD and schizophrenia within a common framework, to quantify their structural similarities. In a novel modification of Anatomical Likelihood Estimation (ALE), 313 foci were extracted from 25 voxel-based studies comprising 660 participants (308 ASD, 352 first-episode schizophrenia) and 801 controls. The results revealed that, compared to controls, lower grey matter volumes within limbic-striato-thalamic circuitry were common to ASD and schizophrenia. Unique features of each disorder included lower grey matter volume in amygdala, caudate, frontal and medial gyrus for schizophrenia and putamen for autism. Thus, in terms of brain volumetrics, ASD and schizophrenia have a clear degree of overlap that may reflect shared etiological mechanisms. However, the distinctive neuroanatomy also mapped in each condition raises the question about how this is arrived in the context of common etiological pressures.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
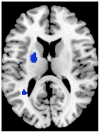

Similar articles
-
Neural circuit disruptions of eye gaze processing in autism spectrum disorder and schizophrenia: An activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis.Schizophr Res. 2024 Feb;264:298-313. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2023.12.003. Epub 2024 Jan 11. Schizophr Res. 2024. PMID: 38215566 Free PMC article.
-
Structural brain abnormalities in adolescents with autism spectrum disorder and patients with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2007 Dec;48(12):1251-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2007.01799.x. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 18093031
-
Anatomical likelihood estimation meta-analysis of grey and white matter anomalies in autism spectrum disorders.Neuroimage Clin. 2014 Nov 18;7:525-36. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2014.11.004. eCollection 2015. Neuroimage Clin. 2014. PMID: 25844306 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroimaging in autistic spectrum disorder (ASD).J Neuroimaging. 2004 Jan;14(1):8-15. J Neuroimaging. 2004. PMID: 14748203 Review.
-
The Role of the Subplate in Schizophrenia and Autism: A Systematic Review.Neuroscience. 2019 Jun 1;408:58-67. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.03.049. Epub 2019 Mar 29. Neuroscience. 2019. PMID: 30930130
Cited by
-
Comparison of children with autism spectrum disorder with and without schizophrenia spectrum traits: gender, season of birth, and mental health risk factors.J Autism Dev Disord. 2012 Nov;42(11):2285-96. doi: 10.1007/s10803-012-1473-4. J Autism Dev Disord. 2012. PMID: 22361923
-
Symptoms of autism and schizophrenia spectrum disorders in clinically referred youth with oppositional defiant disorder.Res Dev Disabil. 2012 Jul-Aug;33(4):1157-68. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2012.01.004. Epub 2012 Mar 22. Res Dev Disabil. 2012. PMID: 22502841 Free PMC article.
-
Psychiatric Polygenic Risk Scores as Predictor for Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Autism Spectrum Disorder in a Clinical Child and Adolescent Sample.Behav Genet. 2020 Jul;50(4):203-212. doi: 10.1007/s10519-019-09965-8. Epub 2019 Jul 25. Behav Genet. 2020. PMID: 31346826 Free PMC article.
-
Neurological abnormalities in recent-onset schizophrenia and asperger-syndrome.Front Psychiatry. 2014 Aug 6;5:91. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2014.00091. eCollection 2014. Front Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 25147527 Free PMC article.
-
Design of a Virtual Reality System for Affect Analysis in Facial Expressions (VR-SAAFE); Application to Schizophrenia.IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2017 Jun;25(6):739-749. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2016.2591556. Epub 2016 Jul 14. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2017. PMID: 27429438 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ghaziuddin M. A family history study of Asperger syndrome. J Autism Dev Disord. 2005;35:177–182. - PubMed
-
- Daniels JL, Forssen U, Hultman CM, Cnattingius S, Savitz DA, et al. Parental psychiatric disorders associated with autism spectrum disorders in the offspring. Pediatrics. 2008;121:e1357–1362. - PubMed
-
- Larsson HJ, Eaton WW, Madsen KM, Vestergaard M, Olesen AV, et al. Risk factors for autism: perinatal factors, parental psychiatric history, and socioeconomic status. Am J Epidemiol. 2005;161:916–925; discussion 926–918. - PubMed
-
- Burbach JP, van der Zwaag B. Contact in the genetics of autism and schizophrenia. Trends Neurosci. 2009;32:69–72. - PubMed
-
- Goodman AB. A family history study of schizophrenia spectrum disorders suggests new candidate genes in schizophrenia and autism. Psychiatr Q. 1994;65:287–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

