Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is mechanistically linked with stem cell signatures in prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 20805998
- PMCID: PMC2929211
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012445
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is mechanistically linked with stem cell signatures in prostate cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Current management of patients diagnosed with prostate cancer (PCa) is very effective; however, tumor recurrence with Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer (CRPC) and subsequent metastasis lead to poor survival outcome, suggesting that there is a dire need for novel mechanistic understanding of tumor recurrence, which would be critical for designing novel therapies. The recurrence and the metastasis of PCa are tightly linked with the biology of prostate cancer stem cells or cancer-initiating cells that is reminiscent of the acquisition of Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) phenotype. Increasing evidence suggests that EMT-type cells share many biological characteristics with cancer stem-like cells.
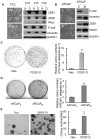
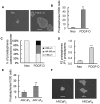
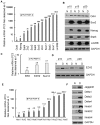
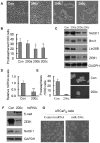
Methodology/principal findings: In this study, we found that PCa cells with EMT phenotype displayed stem-like cell features characterized by increased expression of Sox2, Nanog, Oct4, Lin28B and/or Notch1, consistent with enhanced clonogenic and sphere (prostasphere)-forming ability and tumorigenecity in mice, which was associated with decreased expression of miR-200 and/or let-7 family. Reversal of EMT by re-expression of miR-200 inhibited prostasphere-forming ability of EMT-type cells and reduced the expression of Notch1 and Lin28B. Down-regulation of Lin28B increased let-7 expression, which was consistent with repressed self-renewal capability.
Conclusions/significance: These results suggest that miR-200 played a pivotal role in linking the characteristics of cancer stem-like cells with EMT-like cell signatures in PCa. Selective elimination of cancer stem-like cells by reversing the EMT phenotype to Mesenchymal-Epithelial Transition (MET) phenotype using novel agents would be useful for the prevention of tumor recurrence especially by eliminating those cells that are the "Root Cause" of tumor development and recurrence.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
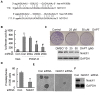
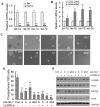
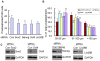
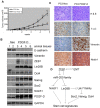
References
-
- Visvader JE, Lindeman GJ. Cancer stem cells in solid tumours: accumulating evidence and unresolved questions. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:755–768. - PubMed
-
- Roudier MP, True LD, Higano CS, Vesselle H, Ellis W, et al. Phenotypic heterogeneity of end-stage prostate carcinoma metastatic to bone. Hum Pathol. 2003;34:646–653. - PubMed
-
- Aoi T, Yae K, Nakagawa M, Ichisaka T, Okita K, et al. Generation of pluripotent stem cells from adult mouse liver and stomach cells. Science. 2008;321:699–702. - PubMed
-
- Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto K, ntosiewicz-Bourget J, Frane JL, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science. 2007;318:1917–1920. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

