The expression of cytokines in the aqueous humor and serum during endotoxin-induced uveitis in C3H/HeN mice
- PMID: 20806043
- PMCID: PMC2927430
The expression of cytokines in the aqueous humor and serum during endotoxin-induced uveitis in C3H/HeN mice
Abstract
Purpose: The cytokines present in the aqueous humor and serum of C3H/HeN mice with endotoxin-induced acute anterior uveitis were analyzed, and the potential role of the cytokines in the pathogenesis of the disease was investigated.
Methods: One hundred and eighty C3H/HeN mice were divided into an experimental group (n=150) and a control group (n=30). The mice in the experimental group were footpad-injected with 200 microg Vibro cholerae endotoxin (classical biotype, serotype Ogawa). The mice were then executed 4 h, 8 h, 16 h, 24 h, and 48 h after the injection of endotoxin. Aqueous humor and peripheral blood samples were collected using a microinjector. Ten samples were pooled together for analysis and centrifuged at 705x g, at 4 degrees C, for 3 min. The supernatant was collected and stored at -80 degrees C. The concentrations of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-1 (IL-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-10 (IL-10), and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) in the samples were measured using a Cytometric Bead Array (CBA).
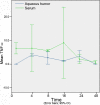
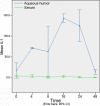
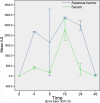
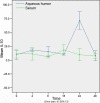
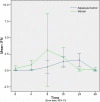
Results: Acute anterior uveitis was successfully induced in C3H/HeN mice. At roughly 16 h post-injection, the concentrations of both IL-1 and IL-6 reached peak levels, and were significantly different from the control group (p=0.001 and p=0.001, respectively). At 24 h post-injection, the concentrations of IFN-gamma and IL-10 in the aqueous humor reached peak levels, and were significantly different from the control group (p=0.022 and p=0.003). The concentrations of IFN-gamma in serum at 4 and 24 hours were significantly different from the control group (p=0.033 and p=0.032). The concentration of IL-10 in serum, at 24 h post-injection, was also found to be significantly different from the control group (p=0.003). The cytokine expression levels in the aqueous humor were consistent with what would be expected during the process of inflammation.
Conclusions: Both IL-1 and IL-6 appear to play an important role in acute anterior uveitis; furthermore, the severity of inflammation may be associated with the dynamic balance of IFN-gamma and IL-10. Our results suggest that the cytokine network might be a useful therapeutic target in the treatment of acute anterior uveitis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Biphasic ocular inflammatory response to endotoxin-induced uveitis in the mouse.Arch Ophthalmol. 2000 Apr;118(4):521-7. doi: 10.1001/archopht.118.4.521. Arch Ophthalmol. 2000. PMID: 10766138
-
The effect of toll-like receptor 4 in the aqueous humor of endotoxin-induced uveitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(2):2110-2118. doi: 10.3390/ijms13022110. Epub 2012 Feb 16. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22408441 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-6 does not mediate endotoxin-induced uveitis in mice: studies in gene deletion animals.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998 Jan;39(1):64-9. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998. PMID: 9430546
-
Temporal sequence of pulmonary cytokine gene expression in response to endotoxin in C3H/HeN endotoxin-sensitive and C3H/HeJ endotoxin-resistant mice.J Leukoc Biol. 1995 Nov;58(5):563-74. doi: 10.1002/jlb.58.5.563. J Leukoc Biol. 1995. PMID: 7595058
-
Analysis of interleukin-6 in endotoxin-induced uveitis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1991 Jan;32(1):88-95. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1991. PMID: 1987109
Cited by
-
LMWH inhibits anterior chamber inflammation after extra capsular lens extraction through down regulation of bFGF content in aqueous humor.Int J Ophthalmol. 2012;5(4):430-3. doi: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2012.04.05. Epub 2012 Aug 18. Int J Ophthalmol. 2012. PMID: 22937500 Free PMC article.
-
Biologic agents in inflammatory eye disease.J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2011 Oct;6(4):309-16. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2011. PMID: 22454752 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Rheum Polysaccharide in the cytokines produced by peripheral blood monocytes in TLR4 mediated HLA-B27 associated AAU.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:431232. doi: 10.1155/2013/431232. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24151602 Free PMC article.
-
The Protective Effect of Low Dose of Lipopolysaccharide Pretreatment on Endotoxin-Induced Uveitis in Rats Is Associated with Downregulation of CSF-1 and Upregulation of LRR-1.J Immunol Res. 2020 Jul 1;2020:9314756. doi: 10.1155/2020/9314756. eCollection 2020. J Immunol Res. 2020. PMID: 32671118 Free PMC article.
-
An anti-interleukin-2 receptor drug attenuates T- helper 1 lymphocytes-mediated inflammation in an acute model of endotoxin-induced uveitis.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 3;9(3):e90216. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090216. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24595020 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sandor F, Buc M. Toll-like Receptors. II. Distribution and Pathways Involved in TLR Signalling. Folia Biol (Praha) 2005;51:188–97. - PubMed
-
- Mashimo H, Ohguro N, Nomura S, Hashida N, Nakai K, Tan Y. Neutrophil Chemotaxis and Local Expression of Interleukin-10 in the Tolerance of Endotoxin-Induced Uveitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008;49:5450–7. - PubMed
-
- Lajavardi L, Bochot A, Camelo S, Goldenberg B, Naud MC, Behar-Cohen F, Fattal E, de Kozak Y. Down regulation of endotoxin-induced uveitis by intravitreal injection of vasoactive intestinal peptide encapsulated in liposomes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007;48:3230–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
