Mapping neuropeptide expression by mass spectrometry in single dissected identified neurons from the dorsal ganglion of the nematode Ascaris suum
- PMID: 20806053
- PMCID: PMC2929024
- DOI: 10.1021/cn1000217
Mapping neuropeptide expression by mass spectrometry in single dissected identified neurons from the dorsal ganglion of the nematode Ascaris suum
Abstract
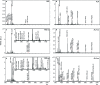
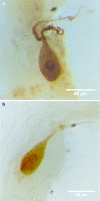
We have developed a method for dissecting single neurons from the nematode Ascaris suum, in order to determine their peptide content by mass spectrometry (MS). In this paper, we use MALDI-TOF MS and tandem MS to enumerate and sequence the peptides present in the two neurons, ALA and RID, that comprise the dorsal ganglion. We compare the peptide content determined by MS with the results of immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridization of previously isolated peptides AF2, AF8 and 6 peptides encoded by the afp-1 transcript. We find complete agreement between the three techniques, which validates single neuron MS as a method for peptide localization. We also discovered and sequenced 6 novel peptides in the ALA neuron. Cloning of cDNAs and database searching of Genomic Survey Sequences showed that transcript afp-12 encodes peptide AF36 (VPSAADMMIRFamide), and afp-13 encodes AF19 (AEGLSSPLIRFamide), AF34 (DSKLMDPLIRFamide), AF35 (DPQQRIVTDETVLRFamide), and 3 non-amidated peptides (PepTT, PepTL, and PepGE). We have found no similarities with reported peptide expression in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. This method promises to be ideally suited for determining the peptide content of each of the 298 neurons in the nervous system of this nematode.
Figures





References
-
- Kotani M.; Detheux M.; Vandenbogaerde A.; Communi D.; Vanderwinden J. M.; Le Poul E.; Brezillon S.; Tyldesley R.; Suarez-Huerta N.; Vandeput F.; Blanpain C.; Schiffmann S. N.; Vassart G.; Parmentier M. (2001) The metastasis suppressor gene KiSS-1 encodes kisspeptins, the natural ligands of the orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR54. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 34631–34636. - PubMed
-
- Cottrell G. A. (1997) The first peptide-gated ion channel. J. Exp. Biol. 200, 2377–2386. - PubMed
-
- Marder E.; Bucher D. (2007) Understanding circuit dynamics using the stomatogastric nervous system of lobsters and crabs. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 69, 291–316. - PubMed
-
- Stretton A.; Donmoyer J.; Davis R.; Meade J.; Cowden C.; Sithigorngul P. (1992) Motor behavior and motor nervous system function in the nematode Ascaris suum. J. Parasitol. 78, 206–214. - PubMed
-
- Davis R. E.; Stretton A. O. (2001) Structure-activity relationships of 18 endogenous neuropeptides on the motor nervous system of the nematode Ascaris suum. Peptides 22, 7–23. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

