Assessing physical activity in persons with knee osteoarthritis using accelerometers: data from the osteoarthritis initiative
- PMID: 20806273
- PMCID: PMC2995807
- DOI: 10.1002/acr.20305
Assessing physical activity in persons with knee osteoarthritis using accelerometers: data from the osteoarthritis initiative
Abstract
Objective: Physical activity measured by accelerometers requires basic assumptions to translate the output into meaningful measures. We used accelerometer data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative to investigate in the context of knee osteoarthritis (OA) the following data processing assumptions derived from the general US adult population: nonwear (a period the monitor was removed), based on zero activity exceeding 60 minutes; and a valid day of monitoring, based on wear time evidence exceeding 10 hours.
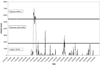
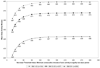
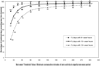
Methods: We examined the influence of nonwear thresholds ranging from 20 to 300 minutes of zero activity on mean daily activity minutes (counts>0), mean daily activity counts, and mean daily moderate to vigorous physical activity minutes. The effect of selecting minimums of 8, 10, or 12 wear hours to signify a valid day of monitoring on data retention was examined.
Results: Our sample of 3,536 days of accelerometer data from 519 persons with knee OA showed that mean daily activity minutes increased with the nonwear threshold until stabilizing at 463 minutes per day, corresponding to the 90-minute nonwear threshold. Similar patterns were observed for mean daily activity counts. Varying the nonwear threshold had no effect on mean daily moderate to vigorous physical activity minutes. Choosing the 90-minute nonwear threshold and a minimum of 10 wear hours to constitute a valid day provided 94% data retention.
Conclusion: Data supported applying the 90-minute nonwear threshold to the knee OA population instead of the 60-minute threshold for the general population, while retaining the 10-hour valid day threshold.
Copyright © 2010 by the American College of Rheumatology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identifying accelerometer nonwear and wear time in older adults.Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2013 Oct 25;10:120. doi: 10.1186/1479-5868-10-120. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2013. PMID: 24156309 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing physical activity in persons with rheumatoid arthritis using accelerometry.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010 Aug;42(8):1493-501. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181cfc9da. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010. PMID: 20139792 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of accelerometer wear and nonwear time classification algorithm.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011 Feb;43(2):357-64. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181ed61a3. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011. PMID: 20581716 Free PMC article.
-
Physical activity levels in patients with early knee osteoarthritis measured by accelerometry.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Sep 15;59(9):1229-36. doi: 10.1002/art.24007. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 18759320 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Potential corner case cautions regarding publicly available implementations of the National Cancer Institute's nonwear/wear classification algorithm for accelerometer data.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 31;13(12):e0210006. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210006. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30596771 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Walking to meet physical activity guidelines in knee osteoarthritis: is 10,000 steps enough?Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2013 Apr;94(4):711-7. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2012.11.038. Epub 2012 Dec 7. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2013. PMID: 23228625 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying accelerometer nonwear and wear time in older adults.Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2013 Oct 25;10:120. doi: 10.1186/1479-5868-10-120. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2013. PMID: 24156309 Free PMC article.
-
Is the association between physical activity and fatigue mediated by physical function or depressive symptoms in symptomatic knee osteoarthritis? The Multicenter Osteoarthritis Study.Scand J Rheumatol. 2021 Sep;50(5):372-380. doi: 10.1080/03009742.2020.1854850. Epub 2021 Mar 20. Scand J Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33749506 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship between Polypharmacy and Physical Activity in Those with or at Risk of Knee Osteoarthritis.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020 Sep;68(9):2015-2020. doi: 10.1111/jgs.16501. Epub 2020 May 22. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020. PMID: 32441333 Free PMC article.
-
When it hurts, a positive attitude may help: association of positive affect with daily walking in knee osteoarthritis. Results from a multicenter longitudinal cohort study.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012 Sep;64(9):1312-9. doi: 10.1002/acr.21694. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012. PMID: 22504854 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Projected state-specific increases in self-reported doctor-diagnosed arthritis and arthritis-attributable activity limitations--United States, 2005–2030. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2007 May 4;56(17):423–425. - PubMed
-
- Dillon CF, Rasch EK, Gu Q, Hirsch R. Prevalence of knee osteoarthritis in the United States: arthritis data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1991–94. J Rheumatol. 2006 Nov;33(11):2271–2279. - PubMed
-
- Sharma L, Cahue S, Song J, Hayes K, Pai YC, Dunlop D. Physical functioning over three years in knee osteoarthritis: role of psychosocial, local mechanical, and neuromuscular factors 12. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Dec;48:3359–3370. - PubMed
-
- Bassett DR, Jr, Cureton AL, Ainsworth BE. Measurement of daily walking distance-questionnaire versus pedometer 5. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2000 May;32:1018–1023. - PubMed
-
- Conway JM, Seale JL, Jacobs DR, Jr, Irwin ML, Ainsworth BE. Comparison of energy expenditure estimates from doubly labeled water, a physical activity questionnaire, and physical activity records 3. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002 Mar;75:519–525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- N01-AR-2-2261/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR054155/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AR-2-2260/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60-AR48098/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025741/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AR-2-2262/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AR022259/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR055287/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AR022258/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AR022262/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AR022260/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AR-2-2258/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR048748/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AR059412/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR055287/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR048098/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR055278/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AR022261/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AR-2-2259/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025755/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR054155/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21-AR059412/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

