Genetic disorders of ion channels
- PMID: 20806840
- PMCID: PMC6188370
Genetic disorders of ion channels
Abstract
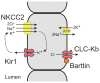
Ion channels play important roles in numerous physiological processes, including the control of heart rate, propagation of the nerve impulse, and insulin secretion. Abnormal functioning of ion channels can cause disease. This article presents an overview of the diseases in humans that are a result of mutations in ion channels.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Ion channels and epilepsy].Rev Neurol. 2000 Jun;30 Suppl 1:S25-41. Rev Neurol. 2000. PMID: 10904966 Review. Spanish.
-
Ion channels-related diseases.Acta Biochim Pol. 2000;47(3):685-703. Acta Biochim Pol. 2000. PMID: 11310970 Review.
-
Ataxia, arrhythmia and ion-channel gene defects.Trends Genet. 1998 Mar;14(3):92-8. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(97)01370-x. Trends Genet. 1998. PMID: 9540405 Review.
-
Molecular diversity of ion channels and cell function.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999 Apr 30;868:1-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb11269.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999. PMID: 10414277 No abstract available.
-
Channelopathies: ion channel defects linked to heritable clinical disorders.J Med Genet. 2000 Oct;37(10):729-40. doi: 10.1136/jmg.37.10.729. J Med Genet. 2000. PMID: 11015449 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ion Channels and Transporters in Muscle Cell Differentiation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 19;22(24):13615. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413615. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanistic basis for potassium efflux-driven activation of the human NLRP1 inflammasome.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jan 9;121(2):e2309579121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2309579121. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38175865 Free PMC article.
References
-
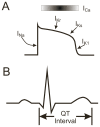
- Morita H, Wu J, Zipes DP. The QT syndromes: long and short. Lancet. 2008;372(9640):750–63. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft FM. Ion Channels and Diseases. Academic Press; 2000.
-
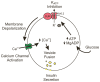
- Koster JC, Permutt MA, Nichols CG. Diabetes and insulin secretion: the ATP-sensitive K+ channel (K ATP) connection. Diabetes. 2005;54(11):3065–72. - PubMed
-
- Huopio H, et al. K(ATP) channels and insulin secretion disorders. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2002;283(2):E207–16. - PubMed
-
- Du W, et al. Calcium-sensitive potassium channelopathy in human epilepsy and paroxysmal movement disorder. Nat Genet. 2005;37(7):733–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical