Importance of the tmRNA system for cell survival when transcription is blocked by DNA-protein cross-links
- PMID: 20807197
- PMCID: PMC2963719
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07355.x
Importance of the tmRNA system for cell survival when transcription is blocked by DNA-protein cross-links
Abstract
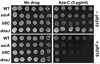
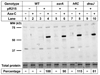
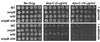
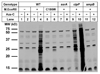
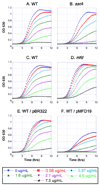
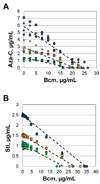
Anticancer drug 5-azacytidine (aza-C) induces DNA-protein cross-links (DPCs) between cytosine methyltransferase and DNA as the drug inhibits methylation. We found that mutants defective in the tmRNA translational quality control system are hypersensitive to aza-C. Hypersensitivity requires expression of active methyltransferase, indicating the importance of DPC formation. Furthermore, the tmRNA pathway is activated upon aza-C treatment in cells expressing methyltransferase, resulting in increased levels of SsrA tagged proteins. These results argue that the tmRNA pathway clears stalled ribosome-mRNA complexes generated after transcriptional blockage by aza-C-induced DPCs. In support, an ssrA mutant is also hypersensitive to streptolydigin, which blocks RNA polymerase elongation by a different mechanism. The tmRNA pathway is thought to act only on ribosomes containing a 3' RNA end near the A site, and the known pathway for releasing RNA 3' ends from a blocked polymerase involves Mfd helicase. However, an mfd knockout mutant is not hypersensitive to either aza-C-induced DPC formation or streptolydigin, indicating that Mfd is not involved. Transcription termination factor Rho is also likely not involved, because the Rho-specific inhibitor bicyclomycin failed to show synergism with either aza-C or streptolydigin. Based on these findings, we discuss models for how E. coli processes transcription/translation complexes blocked at DPCs.
© 2010 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Abo T, Ueda K, Sunohara T, Ogawa K, Aiba H. SsrA-mediated protein tagging in the presence of miscoding drugs and its physiological role in Escherichia coli. Genes to Cells. 2002;7:629–638. - PubMed
-
- Bandaru B, Gopal J, Bhagwat AS. Overproduction of DNA cytosine methyltransferases causes methylation and C->T mutations at non-canonical sites. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:7851–7859. - PubMed
-
- Barbe J, Gibert I, Guerrero R. 5-Azacytidine - Survival and induction of the SOS response in Escherichia coli K-12. Mutat Res. 1986;166:9–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

