Niemann-Pick type C disease: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic approaches
- PMID: 20807315
- PMCID: PMC3008286
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06976.x
Niemann-Pick type C disease: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic approaches
Abstract
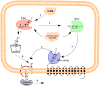
Cholesterol is an important lipid of mammalian cells. Its unique physicochemical properties modulate membrane behavior and it serves as the precursor for steroid hormones, oxysterols and vitamin D. Cholesterol is effluxed from the late endosomes/lysosomes via the concerted action of at least two distinct proteins: Niemann-Pick C (NPC)1 and NPC2. Mutations in these two proteins manifest as NPC disease - a very rare, usually fatal, autosomal, recessive, neurovisceral, lysosomal storage disorder. In this review, we discuss the possible mechanisms of action for NPC1 and NPC2 in mediating cholesterol efflux, as well as the different therapeutic approaches being pursued for the treatment of this lipid storage disorder.
© 2011 The Authors. Journal of Neurochemistry © 2011 International Society for Neurochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson RA, Bryson GM, Parks JS. Lysosomal acid lipase mutations that determine phenotype in Wolman and cholesterol ester storage disease. Mol Genet Metab. 1999;68:333–345. - PubMed
-
- Anderson RA, Sando GN. Cloning and expression of cDNA encoding human lysosomal acid lipase/cholesteryl ester hydrolase. Similarities to gastric and lingual lipases. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:22479–22484. - PubMed
-
- Assmann G, Seedorf U. Acid Lipase Deficiency: Wolman Disease and Cholesteryl Ester Storage Disease. In: Valle B, Vogelstein, Kinzler, Antonarakis, Ballabio, editors. The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. McGraw-Hill; New York: 1995.
-
- Balch WE, Morimoto RI, Dillin A, Kelly JW. Adapting proteostasis for disease intervention. Science. 2008;319:916–919. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

