Dynamic analysis of CD127 expression on memory CD8 T cells from patients with chronic hepatitis B during telbivudine treatment
- PMID: 20807412
- PMCID: PMC2939562
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-207
Dynamic analysis of CD127 expression on memory CD8 T cells from patients with chronic hepatitis B during telbivudine treatment
Abstract
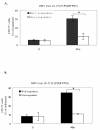
Background: Accumulating evidence supports the theory that expression of CD127 on CD8 T cells during the process of antiviral immune response indicates a subset of effect CD8 T cells that successfully develop into fully protective memory. CD8 T cells expression of CD127 may be used as a predictor to evaluate disease status in chronic viral infection. The aim of this study was to investigate the CD127 expression level on different subsets of CD8 T cell and explore the relationship between CD127 expression on CD8 memory T cells and serum hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA and hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) levels in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB). We also aimed to investigate the CD127 expression pattern on CD8 memory T cells of CHB patients who were treated with Telbivudine.
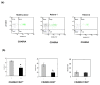
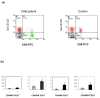
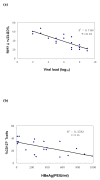
Methods/results: Twenty HBeAg-positive CHB patients were selected and treated with telbivudine 600 mg/day for 48 weeks. The memory CD8 T cells were characterized by expression of CD45RA and CD27 markers. CD127 expression on the CD8 T-cell surface was measured by four-colour flow cytometry. Our results showed that CD127 expression on memory CD8 T cells was reduced in CHB patients. There was a strong negative correlation between CD127 expression on memory CD8 T cells and serum HBV DNA and HBeAg levels in CHB patients. Moreover, successful antiviral therapy increased CD127 expression on CD8 memory T cells as well as on HBV-specific CD8 T cells in CHB patients.
Conclusion: These results suggest that diminished CD127 expression on CD8 memory T cells of CHB patients is a potential mechanism explaining cellular immune function impairment in CHB infection, and that CD127 expression on CD8 memory T cells is a useful indicator for evaluating the effects of anti-HBV therapy.
Figures
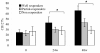
Similar articles
-
Treatment with telbivudine positively regulates antiviral immune profiles in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Mar;57(3):1304-11. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02181-12. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23274669 Free PMC article.
-
[Programmed death-1 (PD-1) and PD-L1 expression during antiviral treatment of chronic hepatitis B].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2010 Sep;18(9):646-50. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2010.09.002. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 20943073 Chinese.
-
Viral infection parameters not nucleoside analogue itself correlates with host immunity in nucleoside analogue therapy for chronic hepatitis B.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jul 28;20(28):9486-96. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i28.9486. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25071343 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Telbivudine: a review of its use in compensated chronic hepatitis B.Drugs. 2010 Oct 1;70(14):1857-83. doi: 10.2165/11204330-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20836578 Review.
-
Telbivudine treatment is associated with high hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion and immune modulatory effects in chronic hepatitis B patients.J Viral Hepat. 2013 Apr;20 Suppl 1:9-17. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12059. J Viral Hepat. 2013. PMID: 23458520 Review.
Cited by
-
Osteopontin promotes dendritic cell maturation and function in response to HBV antigens.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Jun 12;9:3003-16. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S81656. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26109844 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity of twenty peptides representing epitopes of the hepatitis B core and surface antigens by IFN-γ response in chronic and resolved HBV.BMC Immunol. 2015 Nov 2;16:65. doi: 10.1186/s12865-015-0127-7. BMC Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26526193 Free PMC article.
-
IL-7 producing immunotherapy improves ex vivo T cell functions of immunosenescent patients, especially post hip fracture.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023 Aug 1;19(2):2232247. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2232247. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023. PMID: 37417353 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin E2 promotes features of replicative senescence in chronically activated human CD8+ T cells.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 11;9(6):e99432. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099432. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24918932 Free PMC article.
-
Pegylated interferon α enhances recovery of memory T cells in e antigen positive chronic hepatitis B patients.Virol J. 2012 Nov 16;9:274. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-274. Virol J. 2012. PMID: 23158844 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

