Insulin-like 6 is induced by muscle injury and functions as a regenerative factor
- PMID: 20807758
- PMCID: PMC2975228
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.160879
Insulin-like 6 is induced by muscle injury and functions as a regenerative factor
Abstract
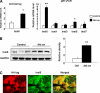
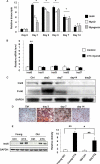
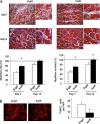
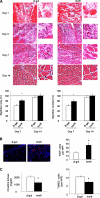
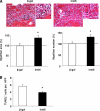
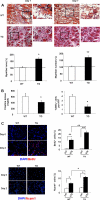
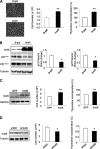
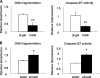
The insulin-like family of factors are involved in the regulation of a variety of physiological processes, but the function of the family member termed insulin-like 6 (Insl6) in skeletal muscle has not been reported. We show that Insl6 is a myokine that is up-regulated in skeletal muscle downstream of Akt signaling and in regenerating muscle in response to cardiotoxin (CTX)-induced injury. In the CTX injury model, myofiber regeneration was improved by the intramuscular or systemic delivery of an adenovirus expressing Insl6. Skeletal muscle-specific Insl6 transgenic mice exhibited normal muscle mass under basal conditions but elevated satellite cell activation and enhanced muscle regeneration in response to CTX injury. The Insl6-mediated regenerative response was associated with reductions in muscle cell apoptosis and reduced serum levels of creatine kinase M. Overexpression of Insl6 stimulated proliferation and reduced apoptosis in cultured myogenic cells. Conversely, knockdown of Insl6 reduced proliferation and increased apoptosis. These data indicate that Insl6 is an injury-regulated myokine that functions as a myogenic regenerative factor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Skeletal Muscle Regeneration in Cardiotoxin-Induced Muscle Injury Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 2;23(21):13380. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113380. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Xin, an actin binding protein, is expressed within muscle satellite cells and newly regenerated skeletal muscle fibers.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007 Nov;293(5):C1636-44. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00124.2007. Epub 2007 Sep 13. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17855775
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling is involved in skeletal muscle regeneration.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010 Mar;298(3):C550-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00072.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 30. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20042733
-
Effects of functional overloading on the regenerative potential of injured skeletal muscles in mice.J Gravit Physiol. 2007 Jul;14(1):P101-2. J Gravit Physiol. 2007. PMID: 18372719
-
Myotoxic phospholipases A2 and the regeneration of skeletal muscles.Toxicon. 2003 Dec 15;42(8):933-45. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2003.11.011. Toxicon. 2003. PMID: 15019492 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Myokines in Myositis Pathogenesis and Their Potential to be New Therapeutic Targets in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies.J Immunol Res. 2020 Jul 24;2020:9079083. doi: 10.1155/2020/9079083. eCollection 2020. J Immunol Res. 2020. PMID: 32775472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skeletal Muscle Regeneration in Cardiotoxin-Induced Muscle Injury Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 2;23(21):13380. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113380. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myocardial Infarction-Induced INSL6 Decrease Contributes to Breast Cancer Progression.Dis Markers. 2023 Feb 7;2023:8702914. doi: 10.1155/2023/8702914. eCollection 2023. Dis Markers. 2023. PMID: 36798786 Free PMC article.
-
The myokine Fibcd1 is an endogenous determinant of myofiber size and mitigates cancer-induced myofiber atrophy.Nat Commun. 2022 May 2;13(1):2370. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30120-1. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35501350 Free PMC article.
-
Myonectin (CTRP15), a novel myokine that links skeletal muscle to systemic lipid homeostasis.J Biol Chem. 2012 Apr 6;287(15):11968-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.336834. Epub 2012 Feb 17. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22351773 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

