Dissecting the biological role of mucin-type O-glycosylation using RNA interference in Drosophila cell culture
- PMID: 20807760
- PMCID: PMC2966062
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.133561
Dissecting the biological role of mucin-type O-glycosylation using RNA interference in Drosophila cell culture
Abstract
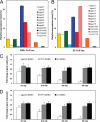
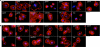
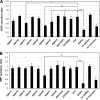
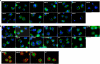
Mucin type O-glycosylation is a highly conserved form of post-translational modification initiated by the family of enzymes known as the polypeptide α-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferases (ppGalNAcTs in mammals and PGANTs in Drosophila). To address the cellular functions of the many PGANT family members, RNA interference (RNAi) to each pgant gene was performed in two independent Drosophila cell culture lines. We demonstrate that RNAi to individual pgant genes results in specific reduction in gene expression without affecting the expression of other family members. Cells with reduced expression of individual pgant genes were then examined for changes in viability, morphology, adhesion, and secretion to assess the contribution of each family member to these cellular functions. Here we find that RNAi to pgant3, pgant6, or pgant7 resulted in reduced secretion, further supporting a role for O-glycosylation in proper secretion. Additionally, RNAi to pgant3 or pgant6 resulted in altered Golgi organization, suggesting a role for each in establishing or maintaining proper secretory apparatus structure. Other subcellular effects observed included multinucleated cells seen after RNAi to either pgant2 or pgant35A, suggesting a role for these genes in the completion of cytokinesis. These studies demonstrate the efficient and specific knockdown of pgant gene expression in two Drosophila cell culture systems, resulting in specific morphological and functional effects. Our work provides new information regarding the biological roles of O-glycosylation and illustrates a new platform for interrogating the cellular and subcellular effects of this form of post-translational modification.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

