The carboxyl-terminal end of Cox1 is required for feedback assembly regulation of Cox1 synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondria
- PMID: 20807763
- PMCID: PMC2966052
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.161976
The carboxyl-terminal end of Cox1 is required for feedback assembly regulation of Cox1 synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondria
Abstract
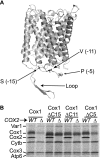
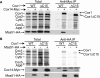
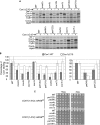
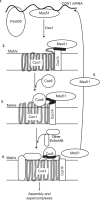
Synthesis of the largest cytochrome c oxidase (CcO) subunit, Cox1, on yeast mitochondrial ribosomes is coupled to assembly of CcO. The translational activator Mss51 is sequestered in early assembly intermediate complexes by an interaction with Cox14 that depends on the presence of newly synthesized Cox1. If CcO assembly is prevented, the level of Mss51 available for translational activation is reduced. We deleted the C-terminal 11 or 15 residues of Cox1 by site-directed mutagenesis of mtDNA. Although these deletions did not prevent respiratory growth of yeast, they eliminated the assembly-feedback control of Cox1 synthesis. Furthermore, these deletions reduced the strength of the Mss51-Cox14 interaction as detected by co-immunoprecipitation, confirming the importance of the Cox1 C-terminal residues for Mss51 sequestration. We surveyed a panel of mutations that block CcO assembly for the strength of their effect on Cox1 synthesis, both by pulse labeling and expression of the ARG8(m) reporter fused to COX1. Deletion of the nuclear gene encoding Cox6, one of the first subunits to be added to assembling CcO, caused the most severe reduction in Cox1 synthesis. Deletion of the C-terminal 15 amino acids of Cox1 increased Cox1 synthesis in the presence of each of these mutations, except pet54. Our data suggest a novel activity of Pet54 required for normal synthesis of Cox1 that is independent of the Cox1 C-terminal end.
Figures
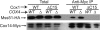
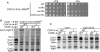
Similar articles
-
Cox25 teams up with Mss51, Ssc1, and Cox14 to regulate mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 expression and assembly in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 7;286(1):555-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.188805. Epub 2010 Nov 10. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21068384 Free PMC article.
-
The Cox1 C-terminal domain is a central regulator of cytochrome c oxidase biogenesis in yeast mitochondria.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jun 30;292(26):10912-10925. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.773077. Epub 2017 May 10. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28490636 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Function of Pet54 in Regulation of Cox1 Synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mitochondria.J Biol Chem. 2016 Apr 22;291(17):9343-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.721985. Epub 2016 Feb 29. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26929411 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenesis of cytochrome oxidase-sophisticated assembly lines in the mitochondrial inner membrane.Gene. 2005 Jul 18;354:43-52. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.03.017. Gene. 2005. PMID: 15905047 Review.
-
Biogenesis and assembly of eukaryotic cytochrome c oxidase catalytic core.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jun;1817(6):883-97. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2011.09.005. Epub 2011 Sep 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 21958598 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The cytochrome b carboxyl terminal region is necessary for mitochondrial complex III assembly.Life Sci Alliance. 2023 Apr 24;6(7):e202201858. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202201858. Print 2023 Jul. Life Sci Alliance. 2023. PMID: 37094942 Free PMC article.
-
Cox25 teams up with Mss51, Ssc1, and Cox14 to regulate mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 expression and assembly in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 7;286(1):555-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.188805. Epub 2010 Nov 10. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21068384 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Cytochrome c Oxidase Biogenesis Is Regulated by the Redox State of a Heme-Binding Translational Activator.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016 Feb 20;24(6):281-98. doi: 10.1089/ars.2015.6429. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016. PMID: 26415097 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Oma1 protease-mediated proteolysis of Cox1 subunit of cytochrome oxidase in assembly mutants.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 2;287(10):7289-300. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.313148. Epub 2012 Jan 4. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22219186 Free PMC article.
-
The Cox1 C-terminal domain is a central regulator of cytochrome c oxidase biogenesis in yeast mitochondria.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jun 30;292(26):10912-10925. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.773077. Epub 2017 May 10. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28490636 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

