Joint functions of protein residues and NADP(H) in oxygen activation by flavin-containing monooxygenase
- PMID: 20807767
- PMCID: PMC2966116
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.161372
Joint functions of protein residues and NADP(H) in oxygen activation by flavin-containing monooxygenase
Abstract
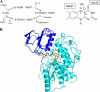
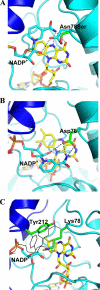
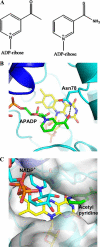
The reactivity of flavoenzymes with dioxygen is at the heart of a number of biochemical reactions with far reaching implications for cell physiology and pathology. Flavin-containing monooxygenases are an attractive model system to study flavin-mediated oxygenation. In these enzymes, the NADP(H) cofactor is essential for stabilizing the flavin intermediate, which activates dioxygen and makes it ready to react with the substrate undergoing oxygenation. Our studies combine site-directed mutagenesis with the usage of NADP(+) analogues to dissect the specific roles of the cofactors and surrounding protein matrix. The highlight of this "double-engineering" approach is that subtle alterations in the hydrogen bonding and stereochemical environment can drastically alter the efficiency and outcome of the reaction with oxygen. This is illustrated by the seemingly marginal replacement of an Asn to Ser in the oxygen-reacting site, which inactivates the enzyme by effectively converting it into an oxidase. These data rationalize the effect of mutations that cause enzyme deficiency in patients affected by the fish odor syndrome. A crucial role of NADP(+) in the oxygenation reaction is to shield the reacting flavin N5 atom by H-bond interactions. A Tyr residue functions as backdoor that stabilizes this crucial binding conformation of the nicotinamide cofactor. A general concept emerging from this analysis is that the two alternative pathways of flavoprotein-oxygen reactivity (oxidation versus monooxygenation) are predicted to have very similar activation barriers. The necessity of fine tuning the hydrogen-bonding, electrostatics, and accessibility of the flavin will represent a challenge for the design and development of oxidases and monoxygenases for biotechnological applications.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functional interactions in cytochrome P450BM3. Evidence that NADP(H) binding controls redox potentials of the flavin cofactors.Biochemistry. 2000 Oct 17;39(41):12699-707. doi: 10.1021/bi001068u. Biochemistry. 2000. PMID: 11027150
-
Role of Ser-257 in the sliding mechanism of NADP(H) in the reaction catalyzed by the Aspergillus fumigatus flavin-dependent ornithine N5-monooxygenase SidA.J Biol Chem. 2013 Nov 8;288(45):32440-32448. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.487181. Epub 2013 Sep 26. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24072704 Free PMC article.
-
Electron transfer in flavocytochrome P450 BM3: kinetics of flavin reduction and oxidation, the role of cysteine 999, and relationships with mammalian cytochrome P450 reductase.Biochemistry. 2003 Sep 16;42(36):10809-21. doi: 10.1021/bi034562h. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12962506
-
Oxygen-transfer reactions by enzymatic flavin-N5 oxygen adducts-Oxidation is not a must.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2024 Jun;80:102464. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2024.102464. Epub 2024 May 12. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 38739969 Review.
-
The devil is in the details: The chemical basis and mechanistic versatility of flavoprotein monooxygenases.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2021 Feb 15;698:108732. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108732. Epub 2020 Dec 24. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2021. PMID: 33358998 Review.
Cited by
-
The Origin and Evolution of Baeyer-Villiger Monooxygenases (BVMOs): An Ancestral Family of Flavin Monooxygenases.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 10;10(7):e0132689. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132689. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26161776 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution to catalysis of ornithine binding residues in ornithine N5-monooxygenase.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015 Nov 1;585:25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2015.09.008. Epub 2015 Sep 12. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015. PMID: 26375201 Free PMC article.
-
The substrate-bound crystal structure of a Baeyer-Villiger monooxygenase exhibits a Criegee-like conformation.J Am Chem Soc. 2012 May 9;134(18):7788-95. doi: 10.1021/ja211876p. Epub 2012 Apr 27. J Am Chem Soc. 2012. PMID: 22506764 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the Protein Matrix: Probing Cofactor Variants in a Baeyer-Villiger Oxygenation Reaction.ACS Catal. 2013;3(12):3058-3062. doi: 10.1021/cs400837z. ACS Catal. 2013. PMID: 24443704 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen peroxide elimination from C4a-hydroperoxyflavin in a flavoprotein oxidase occurs through a single proton transfer from flavin N5 to a peroxide leaving group.J Biol Chem. 2011 May 13;286(19):16900-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.222976. Epub 2011 Mar 19. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21454569 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cashman J. R., Zhang J. (2006) Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 46, 65–100 - PubMed
-
- Phillips I. R., Shephard E. A. (2008) Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 29, 294–301 - PubMed
-
- Schlaich N. L. (2007) Trends Plant Sci. 12, 412–448 - PubMed
-
- Al-Waiz M., Ayesh R., Mitchell S. C., Idle J. R., Smith R. L. (1987) Lancet. 1, 634–635 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

