Bone marrow myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) inhibit graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) via an arginase-1-dependent mechanism that is up-regulated by interleukin-13
- PMID: 20807889
- PMCID: PMC3031417
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-06-287839
Bone marrow myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) inhibit graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) via an arginase-1-dependent mechanism that is up-regulated by interleukin-13
Abstract
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) are a well-defined population of cells that accumulate in the tissue of tumor-bearing animals and are known to inhibit immune responses. Within 4 days, bone marrow cells cultured in granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor resulted in the generation of CD11b(+)Ly6G(lo)Ly6C(+) MDSCs, the majority of which are interleukin-4Rα (IL-4Rα(+)) and F4/80(+). Such MDSCs potently inhibited in vitro allogeneic T-cell responses. Suppression was dependent on L-arginine depletion by arginase-1 activity. Exogenous IL-13 produced an MDSC subset (MDSC-IL-13) that was more potently suppressive and resulted in arginase-1 up-regulation. Suppression was reversed with an arginase inhibitor or on the addition of excess L-arginine to the culture. Although both MDSCs and MDSC-IL-13 inhibited graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) lethality, MDSC-IL-13 were more effective. MDSC-IL-13 migrated to sites of allopriming. GVHD inhibition was associated with limited donor T-cell proliferation, activation, and proinflammatory cytokine production. GVHD inhibition was reduced when arginase-1-deficient MDSC-IL-13 were used. MDSC-IL-13 did not reduce the graft-versus-leukemia effect of donor T cells. In vivo administration of a pegylated form of human arginase-1 (PEG-arg1) resulted in L-arginine depletion and significant GVHD reduction. MDSC-IL-13 and pegylated form of human arginase-1 represent novel strategies to prevent GVHD that can be clinically translated.
Figures


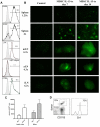



Comment in
-
Exploiting arginase to prevent GVHD.Blood. 2010 Dec 16;116(25):5440-1. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-09-306431. Blood. 2010. PMID: 21163935 No abstract available.
References
-
- Nagaraj S, Gabrilovich DI. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;601:213–223. - PubMed
-
- Movahedi K, Guilliams M, Van den Bossche J, et al. Identification of discrete tumor-induced myeloid-derived suppressor cell subpopulations with distinct T cell-suppressive activity. Blood. 2008;111(8):4233–4244. - PubMed
-
- Huang B, Pan PY, Li Q, et al. Gr-1+CD115+ immature myeloid suppressor cells mediate the development of tumor-induced T regulatory cells and T-cell anergy in tumor-bearing host. Cancer Res. 2006;66(2):1123–1131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 AI056299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL49997/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI034495/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI34495/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103501/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA107974/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA142106/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL56067/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL049997/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR021970/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA082689/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL056067/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL056067/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

