An ultrasound contrast agent targeted to P-selectin detects activated platelets at supra-arterial shear flow conditions
- PMID: 20808239
- PMCID: PMC3426507
- DOI: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3181ed1b3b
An ultrasound contrast agent targeted to P-selectin detects activated platelets at supra-arterial shear flow conditions
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate targeting of a microbubble contrast agent to platelets under high shear flow using the natural selectin ligand sialyl Lewis.
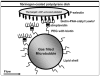
Materials and methods: Biotinylated polyacrylamide Sialyl Lewis or biotinylated carbohydrate-free polymer (used as a control) were attached to biotinylated microbubbles via a streptavidin linker. Activated human platelets were isolated and attached to fibrinogen-coated culture dishes. Fibrinogen-coated dishes without platelets or platelet dishes blocked by an anti-P-selectin antibody served as negative control substrates. Dishes coated by recombinant P-selectin served as a positive control substrate. Microbubble adhesion was assessed by microscopy in an inverted parallel plate flow chamber, with wall shear stress values of 40, 30, 20, 10, and 5 dynes/cm2. The ratio of binding and passing microbubbles was defined as capture efficiency.
Results: There was no significant difference between the groups regarding the number of microbubbles in the fluid flow at each shear rate. Sialyl Lewis-targeted microbubbles were binding and slowly rolling on the surface of activated platelets and P-selectin-coated dishes at all the flow conditions including 40 dynes/cm2. Capture efficiency of targeted microbubbles to activated platelets and recombinant P-selectin decreased with increasing shear flow: at 5 dynes/cm2, capture efficiency was 16.11% on activated platelets versus 21.83% on P-selectin, and, at 40 dynes/cm2, adhesion efficiency was still 3.4% in both groups. There was neither significant adhesion of Sialyl Lewis-targeted microbubbles to control substrates, nor adhesion of control microbubbles to activated platelets or to recombinant P-selectin.
Conclusions: Microbubble targeting using sialyl Lewis, a fast-binding ligand to P-selectin, is a promising strategy for the design of ultrasound contrast binding to activated platelets under high shear stress conditions.
Figures

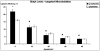
References
-
- von zur Muhlen C, von Elverfeldt D, Moeller JA, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent targeted toward activated platelets allows in vivo detection of thrombosis and monitoring of thrombolysis. Circulation. 2008;118:258–267. - PubMed
-
- Corti R, Farkouh ME, Badimon JJ. The vulnerable plaque and acute coronary syndromes. Am J Med. 2002;113:668–680. - PubMed
-
- Stary HC, Chandler AB, Dinsmore RE, et al. A definition of advanced types of atherosclerotic lesions and a histological classification of atherosclerosis. A report from the Committee on Vascular Lesions of the Council on Arteriosclerosis, American Heart Association. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995;15:1512–1531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

