Prognostic significance of AMP-activated protein kinase expression and modifying effect of MAPK3/1 in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 20808308
- PMCID: PMC2965861
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605846
Prognostic significance of AMP-activated protein kinase expression and modifying effect of MAPK3/1 in colorectal cancer
Abstract
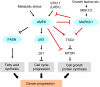
Background: AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK, PRKA) has central roles in cellular metabolic sensing and energy balance homeostasis, and interacts with various pathways (e.g., TP53 (p53), FASN, MTOR and MAPK3/1 (ERK)). AMP-activated protein kinase activation is cytotoxic to cancer cells, supporting AMPK as a tumour suppressor and a potential therapeutic target. However, no study has examined its prognostic role in colorectal cancers.
Methods: Among 718 colon and rectal cancers, phosphorylated AMPK (p-AMPK) and p-MAPK3/1 expression was detected in 409 and 202 tumours, respectively, by immunohistochemistry. Cox proportional hazards model was used to compute mortality hazard ratio (HR), adjusting for clinical and tumoral features, including microsatellite instability, CpG island methylator phenotype, LINE-1 methylation, and KRAS, BRAF and PIK3CA mutations.
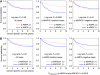
Results: Phosphorylated AMPK expression was not associated with survival among all patients. Notably, prognostic effect of p-AMPK significantly differed by p-MAPK3/1 status (P(interaction)=0.0017). Phosphorylated AMPK expression was associated with superior colorectal cancer-specific survival (adjusted HR 0.42; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.24-0.74) among p-MAPK3/1-positive cases, but not among p-MAPK3/1-negative cases (adjusted HR 1.22; 95% CI: 0.85-1.75).
Conclusion: Phosphorylated AMPK expression in colorectal cancer is associated with superior prognosis among p-MAPK3/1-positive cases, but not among p-MAPK3/1-negative cases, suggesting a possible interaction between the AMPK and MAPK pathways influencing tumour behaviour.
Conflict of interest statement
LCC is Chairman of the Scientific Advisory Board and a minor stockholder of Cell Signaling Technologies, which provides the antibodies against p-AMPK and phospho-p44/42 MAPK that were used in this study. LCC is Founder and Scientific Advisory Board Member of Agios Pharmaceuticals, which has a commercial interest in targeted therapy. No other conflict of interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Beeram M, Patnaik A, Rowinsky EK (2005) Raf: a strategic target for therapeutic development against cancer. J Clin Oncol 23: 6771–6790 - PubMed
-
- Boland CR, Thibodeau SN, Hamilton SR, Sidransky D, Eshleman JR, Burt RW, Meltzer SJ, Rodriguez-Bigas MA, Fodde R, Ranzani GN, Srivastava S (1998) A National Cancer Institute Workshop on Microsatellite Instability for cancer detection and familial predisposition: development of international criteria for the determination of microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 58: 5248–5257 - PubMed
-
- Bowker SL, Majumdar SR, Veugelers P, Johnson JA (2006) Increased cancer-related mortality for patients with type 2 diabetes who use sulfonylureas or insulin. Diabetes Care 29: 254–258 - PubMed
-
- Buzzai M, Jones RG, Amaravadi RK, Lum JJ, DeBerardinis RJ, Zhao F, Viollet B, Thompson CB (2007) Systemic treatment with the antidiabetic drug metformin selectively impairs p53-deficient tumor cell growth. Cancer Res 67: 6745–6752 - PubMed
-
- Chan AT, Ogino S, Fuchs CS (2007) Aspirin and the risk of colorectal cancer in relation to the expression of COX-2. N Engl J Med 356: 2131–2142 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

