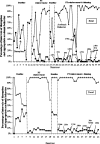
The effects of fixed-time escape on inappropriate and appropriate classroom behavior
- PMID: 20808507
- PMCID: PMC2831445
- DOI: 10.1901/jaba.2010.43-149
The effects of fixed-time escape on inappropriate and appropriate classroom behavior
Abstract
Few studies have explored the effects of fixed-time (FT) reinforcement on escape-maintained behavior of students in a classroom setting. We measured the effects of an FT schedule on the disruptive and appropriate academic behaviors of 2 junior high students in a public school setting. Results demonstrated that FT escape from tasks resulted in a substantial decrease in disruptive behavior and an increase in time engaged in tasks for both participants.
Keywords: escape-maintained behavior; fixed-time reinforcement schedules; function-based interventions; noncontingent reinforcement.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fixed-time teacher attention to decrease off-task behaviors of typically developing third graders.J Appl Behav Anal. 2008 Summer;41(2):279-83. doi: 10.1901/jaba.2008.41-279. J Appl Behav Anal. 2008. PMID: 18595294 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of fixed-time reinforcement schedules on problem behavior of children with emotional and behavioral disorders in a day-treatment classroom setting.J Appl Behav Anal. 2006 Winter;39(4):453-7. doi: 10.1901/jaba.2006.172-05. J Appl Behav Anal. 2006. PMID: 17236344 Free PMC article.
-
Fixed-time schedule effects in combination with response-dependent schedules.J Appl Behav Anal. 2011 Spring;44(1):163-7. doi: 10.1901/jaba.2011.44-163. J Appl Behav Anal. 2011. PMID: 21541131 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence-based interventions for adolescents with disruptive behaviors in school-based settings.Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2015 Apr;24(2):305-17. doi: 10.1016/j.chc.2014.11.005. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2015. PMID: 25773326 Review.
-
Effects of Multiple Schedules of Reinforcement on Appropriate Communication and Challenging Behaviors: A Meta-analysis.J Autism Dev Disord. 2021 Feb;51(2):613-631. doi: 10.1007/s10803-020-04569-2. J Autism Dev Disord. 2021. PMID: 32592096 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparing Visual and Statistical Analysis in Single-Case Studies Using Published Studies.Multivariate Behav Res. 2015;50(2):162-83. doi: 10.1080/00273171.2014.973989. Multivariate Behav Res. 2015. PMID: 26609876 Free PMC article.
-
Motivating Operations and Negative Reinforcement.Perspect Behav Sci. 2020 Aug 18;43(4):761-778. doi: 10.1007/s40614-020-00266-8. eCollection 2020 Dec. Perspect Behav Sci. 2020. PMID: 33381687 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carr J.E, Coriaty S, Wilder D.A, Gaunt B.T, Dozier C.L, Britton L.N, et al. A review of “noncontingent” reinforcement as treatment for the aberrant behavior of individuals with developmental disabilities. Research in Developmental Disabilities. 2000;21:377–391. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical