Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma: a 13-year experience at a single institution
- PMID: 20808529
- PMCID: PMC2853070
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0029-1236165
Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma: a 13-year experience at a single institution
Abstract
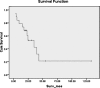
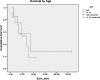
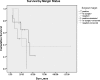
We present our experience with sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma at the University of Michigan over 13 years and review prior published data. We conducted a retrospective review of 19 patients who presented to a tertiary care academic center multidisciplinary skull base clinic with sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma between 1995 and 2008. Overall survival was 22% at 5 years, and the estimated 5-year distant metastasis-free survival was 35%. At 2 years, local control was 83%, regional control was 50%, and distant control was 83%. Local control was best in those patients treated nonsurgically, as was median survival, though this was not statistically significant. Nodal disease in the neck, either at presentation or at recurrence, was noted in 26% of patients. Survival for sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma remains poor. It is possible that up-front radiation or chemoradiation will lead to better local control rates, though surgery remains a mainstay of treatment. In all cases, the cervical nodes should be addressed with primary treatment.
Keywords: SNUC; anterior skull base; sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma; subcranial.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma with intracranial extension.Skull Base. 2006 May;16(2):67-74. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-931621. Skull Base. 2006. PMID: 22496625 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of SMARCB1 Expression Confers Poor Prognosis to Sinonasal Undifferentiated Carcinoma.J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2020 Dec;81(6):610-619. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1693659. Epub 2019 Jul 24. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2020. PMID: 33381364 Free PMC article.
-
Minimally invasive endoscopic resection of sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma.Am J Otolaryngol. 2011 Nov-Dec;32(6):464-9. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2010.09.006. Epub 2010 Oct 30. Am J Otolaryngol. 2011. PMID: 21041001
-
Trimodality management of sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma and review of the literature.Am J Clin Oncol. 2013 Dec;36(6):584-8. doi: 10.1097/COC.0b013e31825eb3a5. Am J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 22992621 Review.
-
Sinonasal Undifferentiated Carcinoma.Curr Oncol Rep. 2019 Feb 26;21(3):26. doi: 10.1007/s11912-019-0776-4. Curr Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30806835 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular profiling of sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma.Head Neck. 2014 Jan;36(1):15-21. doi: 10.1002/hed.23267. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Head Neck. 2014. PMID: 23633104 Free PMC article.
-
Frequent IDH2 R172 mutations in undifferentiated and poorly-differentiated sinonasal carcinomas.J Pathol. 2017 Aug;242(4):400-408. doi: 10.1002/path.4915. Epub 2017 Jun 9. J Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28493366 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of multimodality therapy in the treatment of sinonasal neuroendocrine carcinoma.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013 Sep;270(9):2565-8. doi: 10.1007/s00405-013-2554-5. Epub 2013 Jun 6. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013. PMID: 23740425
-
Definitive-intent (chemo)radiotherapy for sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma.Br J Radiol. 2023 Jan 1;96(1141):20220244. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20220244. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Br J Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36317997 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Adjuvant Treatment in Craniofacial Malignancy: A Critical Review.Front Oncol. 2020 Aug 7;10:1402. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01402. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32850452 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Frierson H F, Jr, Mills S E, Fechner R E, Taxy J B, Levine P A. Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma. An aggressive neoplasm derived from schneiderian epithelium and distinct from olfactory neuroblastoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1986;10:771–779. - PubMed
-
- Gorelick J, Ross D, Marentette L, Blaivas M. Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma: case series and review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 2000;47:750–754. discussion 754–755. - PubMed
-
- Jones L R, Guffey P, Cordell K G, et al. Determination of tumor markers that can be used as prognostic indicators of sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma, esthesioneuroblastoma and adenoid cystic carcinoma of the skull base. Data not yet published.
-
- Musy P Y, Reibel J F, Levine P A. Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma: the search for a better outcome. Laryngoscope. 2002;112(8 Pt 1):1450–1455. - PubMed
-
- Chen A M, Daly M E, El-Sayed I, et al. Patterns of failure after combined-modality approaches incorporating radiotherapy for sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma of the head and neck. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70:338–343. - PubMed