Cotyloplasty in cementless total hip arthroplasty for an insufficient acetabulum
- PMID: 20808585
- PMCID: PMC2915393
- DOI: 10.4055/cios.2010.2.3.148
Cotyloplasty in cementless total hip arthroplasty for an insufficient acetabulum
Abstract
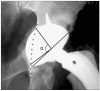
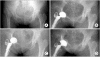
Background: Cotyloplasty is a technique that involves making a perforation of the medial wall of a shallow acetabulum and then inserting an acetabular cup with the medial aspect of its dome beyond the Kohler line. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the results of cementless total hip arthroplasty (THA) using cotyloplasty with focusing on the amount of medial cup protrusion.
Methods: Sixteen hips with insufficient acetabulum in sixteen patients were treated by cementless THA using cotyloplasty. The average patient age was 47 years. The diagnoses included dysplastic hip (12) and infection sequelae (4). All the patients were followed up for at least 2 years. Clinically, the Harris hip scores were assessed and radiologically, the amount of cup protrusion, the hip center movement and cup fixation were evaluated.
Results: The average Harris hip score improved from 57 to 94 postoperatively. The average proportion of cup surface beyond the Kohler line was 44.1% and the hip centers were medialized by an average of 23 mm. Stable fixation of the acetabular cup was achieved in all the cases except one. In this one case, migration of the cup was detected 2 weeks postoperatively and a reoperation was performed.
Conclusions: Using cotyloplasty, good coverage of the acetabular cup was obtained without a block bone graft, and the hip joint centers were medialized. However, the safety margin for the amount of protrusion should be established.
Keywords: Cementless; Cotyloplasty; Hip dysplasia; Insufficient acetbulum; Total hip replacement.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cementless total hip arthroplasty with medial wall osteotomy for the sequelae of septic arthritis of the hip.Clin Orthop Surg. 2009 Mar;1(1):19-26. doi: 10.4055/cios.2009.1.1.19. Epub 2009 Feb 6. Clin Orthop Surg. 2009. PMID: 19884993 Free PMC article.
-
Medial Protrusio Technique in Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty for Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip: A Prospective 6- to 9-Year Follow-Up of 43 Consecutive Patients.J Arthroplasty. 2016 Aug;31(8):1761-6. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2016.01.052. Epub 2016 Feb 9. J Arthroplasty. 2016. PMID: 26948130
-
Medial protrusio technique for placement of a porous-coated, hemispherical acetabular component without cement in a total hip arthroplasty in patients who have acetabular dysplasia.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999 Jan;81(1):83-92. doi: 10.2106/00004623-199901000-00012. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999. PMID: 9973058
-
Total hip arthroplasty in acetabular protrusio.Orthopedics. 2009 Sep;32(9):orthosupersite.com/view.asp?rID=42836. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20090728-12. Orthopedics. 2009. PMID: 19751015 Review.
-
Periacetabular osteotomy in the treatment of severe acetabular dysplasia. Surgical technique.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006 Mar;88 Suppl 1 Pt 1:65-83. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.E.00887. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006. PMID: 16510801 Review.
Cited by
-
Total Hip Replacement in Developmental Hip Dysplasia: A Narrative Review.Cureus. 2021 Apr 29;13(4):e14763. doi: 10.7759/cureus.14763. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34094728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Total hip replacement in developmental dysplasia: anatomical features and technical pitfalls].Orthopade. 2011 Jun;40(6):543-53. doi: 10.1007/s00132-011-1754-1. Orthopade. 2011. PMID: 21562860 German.
-
[Biomechanical research progress of common acetabular reconstruction techniques for Crowe type Ⅱ and Ⅲ developmental dysplasia of the hip].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Mar 15;37(3):353-359. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202211052. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 36940996 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Uncemented Total Hip Replacement After Two Years of Neglected Hip Dislocation With Fracture of Posterior Column and Wall of the Acetabulum.Trauma Mon. 2016 Jul 18;21(5):e25301. doi: 10.5812/traumamon.25301. eCollection 2016 Nov. Trauma Mon. 2016. PMID: 28184362 Free PMC article.
-
A simple technique to strengthen the initial and mid-term to long-term stability of the cup during total hip arthroplasty in developmental dysplasia of the hip.Saudi Med J. 2018 Apr;39(4):342-346. doi: 10.15537/smj.2018.4.21684. Saudi Med J. 2018. PMID: 29619484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Charnley J, Feagin JA. Low-friction arthroplasty in congenital subluxation of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1973;(91):98–113. - PubMed
-
- Dorr LD, Tawakkol S, Moorthy M, Long W, Wan Z. Medial protrusio technique for placement of a porous-coated, hemispherical acetabular component without cement in a total hip arthroplasty in patients who have acetabular dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81(1):83–92. - PubMed
-
- Linde F, Jensen J, Pilgaard S. Charnley arthroplasty in osteoarthritis secondary to congenital dislocation or subluxation of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988;(227):164–171. - PubMed
-
- Morsi E, Garbuz D, Gross AE. Total hip arthroplasty with shelf graft s using uncemented cups: a long-term follow-up study. J Arthroplasty. 1996;11(1):81–85. - PubMed
-
- Spangehl MJ, Berry DJ, Trousdale RT, Cabanela ME. Uncemented acetabular components with bulk femoral head autograft for acetabular reconstruction in developmental dysplasia of the hip: results at five to twelve years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83(10):1484–1489. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

