Efficacy of dendritic cells matured early with OK-432 (Picibanil), prostaglandin E2, and interferon-alpha as a vaccine for a hormone refractory prostate cancer cell line
- PMID: 20808670
- PMCID: PMC2923792
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.9.1284
Efficacy of dendritic cells matured early with OK-432 (Picibanil), prostaglandin E2, and interferon-alpha as a vaccine for a hormone refractory prostate cancer cell line
Abstract
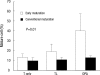
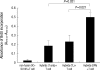
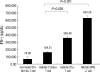
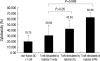
Dendritic cells (DCs) are potent antigen-presenting cells. OK432 (Picibanil) was introduced as a potent stimulator of DC maturation in combination with prostaglandin-E(2) and interferon-alpha. We compared the efficacy of a DC-prostate cancer vaccine using early-mature DCs stimulated with OK432, PGE2 and INF-alpha (OPA) with that of vaccines using other methods. On days 3 or 7 of DC culture, TNF-alpha (T), TNF-alpha and LPS (TL) or OPA were employed as maturation stimulators. DU145 cells subjected to heat stress were hybridized with mature DCs using polyethyleneglycol. T cells were sensitized by the hybrids, and their proliferative and cytokine secretion activities and cytotoxicity were measured. The yields of early-mature DCs were higher, compared to yields at the conventional maturation time (P<0.05). In the early maturation setting, the mean fusion ratios, calculated from the fraction of dual-positive cells, were 13.3%, 18.6%, and 39.9%, respectively (P=0.051) in the T only, TL, and OPA-treated groups. The function of cytotoxic T cells, which were sensitized with the hybrids containing DCs matured early with OPA, was superior to that using other methods. The antitumor effects of DC-DU145 hybrids generated with DCs subjected to early maturation with the OPA may be superior to that of the hybrids using conventional maturation methods.
Keywords: Cancer Vaccines; Dendritic Cells; Immunotherapy; Prostatic Neoplasms.
Figures


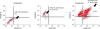
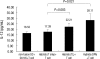
References
-
- Koido S, Hara E, Homma S, Torii A, Mitsunaga M, Yanagisawa S, Toyama Y, Kawahara H, Watanabe M, Yoshida S, Kobayashi S, Yanaga K, Fujise K, Tajiri H. Streptococcal preparation OK-432 promotes fusion efficiency and enhances induction of antigen-specific CTL by fusions of dendritic cells and colorectal cancer cells. J Immunol. 2007;178:613–622. - PubMed
-
- Sakakibara M, Kanto T, Inoue M, Kaimori A, Yakushijin T, Miyatake H, Itose I, Miyazaki M, Kuzushita N, Hiramatsu N, Takehara T, Kasahara A, Hayashi N. Quick generation of fully mature dendritic cells from monocytes with OK432, low-dose prostanoid, and interferon-α as potent immune enhancers. J Immunother. 2006;29:67–77. - PubMed
-
- Koido S, Hara E, Homma S, Mitsunaga M, Takahara A, Nagasaki E, Kawahara H, Watanabe M, Toyama Y, Yanagisawa S, Kobayashi S, Yanaga K, Fujise K, Gong J, Tajiri H. Synergistic induction of antigen-specific CTL by fusion of TLR-stimulated dendritic cells and heat stressed tumor cells. J Immunol. 2007;179:4874–4883. - PubMed
-
- Shu YQ, Gu Y. The effect of dendritic cells activated by OK-432 and pulsed with antigens on cytokine induced killers. Biomed Pharmacother. 2006;60:156–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

