Two cases of transfusion-related acute lung injury triggered by HLA and anti-HLA antibody reaction
- PMID: 20808691
- PMCID: PMC2923780
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.9.1398
Two cases of transfusion-related acute lung injury triggered by HLA and anti-HLA antibody reaction
Abstract
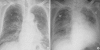
Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) is a serious adverse transfusion reaction that is presented as acute hypoxemia and non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema, which develops during or within 6 hr of transfusion. Major pathogenesis of TRALI is known to be related with anti-HLA class I, anti-HLA class II, or anti-HNA in donor's plasma. However, anti-HLA or anti-HNA in recipient against transfused donor's leukocyte antigens also cause TRALI in minor pathogenesis and which comprises about 10% of TRALI. Published reports of TRALI are relatively rare in Korea. In our cases, both patients presented with dyspnea and hypoxemia during transfusion of packed red blood cells and showed findings of bilateral pulmonary infiltrations at chest radiography. Findings of patients' anti-HLA antibodies and recipients' HLA concordance indicate that minor pathogenesis may be not as infrequent as we'd expected before. In addition, second case showed that anti-HLA class II antibodies could be responsible for immunopathogenic mechanisms, alone.
Keywords: Adverse Transfusion Reaction; Anti-HLA Antibody; Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI).
Figures

Similar articles
-
A possible case of recipient anti-neutrophil and anti-human leukocyte antigen antibody-mediated fatal reverse transfusion-related acute lung injury.Transfusion. 2021 Apr;61(4):1336-1340. doi: 10.1111/trf.16330. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Transfusion. 2021. PMID: 33666248
-
Are we underestimating reverse TRALI?Transfusion. 2019 Sep;59(9):2788-2793. doi: 10.1111/trf.15431. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Transfusion. 2019. PMID: 31241780
-
Mechanisms of transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI): anti-leukocyte antibodies.Crit Care Med. 2006 May;34(5 Suppl):S118-23. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000214293.72918.D8. Crit Care Med. 2006. PMID: 16617255 Review.
-
Implementation and outcomes of a transfusion-related acute lung injury surveillance programme and study of HLA/HNA alloimmunisation in blood donors.Blood Transfus. 2012 Jul;10(3):351-9. doi: 10.2450/2012.0089-11. Epub 2012 Feb 22. Blood Transfus. 2012. PMID: 22395353 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody-mediated transfusion-related acute lung injury; from discovery to prevention.Br J Haematol. 2015 Sep;170(5):597-614. doi: 10.1111/bjh.13459. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Br J Haematol. 2015. PMID: 25921271 Review.
Cited by
-
A case of transfusion-related acute lung injury induced by anti-human leukocyte antigen antibodies in acute leukemia.Korean J Hematol. 2012 Dec;47(4):302-6. doi: 10.5045/kjh.2012.47.4.302. Epub 2012 Dec 24. Korean J Hematol. 2012. PMID: 23320011 Free PMC article.
-
Convalescent Plasma: A Potential Life-Saving Therapy for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19).Front Public Health. 2020 Aug 6;8:437. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00437. eCollection 2020. Front Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32903641 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Convalescent Plasma Therapy in Coronavirus Disease 2019: a Case Report and Suggestions to Overcome Obstacles.J Korean Med Sci. 2020 Jul 6;35(26):e239. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e239. J Korean Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32627442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Danielson C, Benjamin RJ, Mangano MM, Mills CJ, Waxman DA. Pulmonary pathology of rapidly fatal transfusion-related acute lung injury reveals minimal evidence of diffuse alveolar damage or alveolar granulocyte infiltration. Transfusion. 2008;48:2401–2408. - PubMed
-
- Kleinman S, Caulfield T, Chan P, Davenport R, McFarland J, McPhedran S, Meade M, Morrison D, Pinsent T, Robillard P, Slinger P. Toward an understanding of transfusion-related acute lung injury: statement of a consensus panel. Transfusion. 2004;44:1774–1789. - PubMed
-
- Middelburg RA, van Stein D, Briet E, van der Bom JG. The role of donor antibodies in the pathogenesis of transfusion-related acute lung injury: a systematic review. Transfusion. 2008;48:2167–2176. - PubMed
-
- Huh JY, Han TH, Seo JW, Kim DC, Roh DH, Han KS. A case of transfusion-related acute lung injury. Korean J Blood Transfus. 2005;16:250–254.
-
- Li G, Daniels CE, Kojicic M, Krpata T, Wilson GA, Winters JL, Moore SB, Gajic O. The accuracy of natriuretic peptides (brain natriuretic peptide and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic) in the differentiation between transfusion-related acute lung injury and transfusion-related circulatory overload in the critically ill. Transfusion. 2009;49:13–20. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

