IL-6 and IL-10 anti-inflammatory activity links exercise to hypothalamic insulin and leptin sensitivity through IKKbeta and ER stress inhibition
- PMID: 20808781
- PMCID: PMC2927536
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000465
IL-6 and IL-10 anti-inflammatory activity links exercise to hypothalamic insulin and leptin sensitivity through IKKbeta and ER stress inhibition
Retraction in
-
Retraction: IL-6 and IL-10 Anti-Inflammatory Activity Links Exercise to Hypothalamic Insulin and Leptin Sensitivity through IKKβ and ER Stress Inhibition.PLoS Biol. 2023 Apr 4;21(4):e3002079. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002079. eCollection 2023 Apr. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 37015095 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Overnutrition caused by overeating is associated with insulin and leptin resistance through IKKbeta activation and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in the hypothalamus. Here we show that physical exercise suppresses hyperphagia and associated hypothalamic IKKbeta/NF-kappaB activation by a mechanism dependent upon the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-6. The disruption of hypothalamic-specific IL-6 action blocked the beneficial effects of exercise on the re-balance of food intake and insulin and leptin resistance. This molecular mechanism, mediated by physical activity, involves the anti-inflammatory protein IL-10, a core inhibitor of IKKbeta/NF-kappaB signaling and ER stress. We report that exercise and recombinant IL-6 requires IL-10 expression to suppress hyperphagia-related obesity. Moreover, in contrast to control mice, exercise failed to reverse the pharmacological activation of IKKbeta and ER stress in C3H/HeJ mice deficient in hypothalamic IL-6 and IL-10 signaling. Hence, inflammatory signaling in the hypothalamus links beneficial physiological effects of exercise to the central action of insulin and leptin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
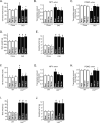
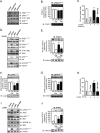
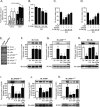
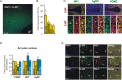


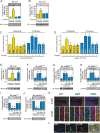
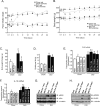

Comment in
-
Metabolism: An appetite for exercise.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010 Oct;11(10):662. doi: 10.1038/nrn2926. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21080528 No abstract available.
References
-
- Carvalheira J. B, Ribeiro E. B, Araujo E. P, Guimaraes R. B, Telles M. M, et al. Selective impairment of insulin signalling in the hypothalamus of obese Zucker rats. Diabetologia. 2003;46:1629–1640. - PubMed
-
- Niswender K. D, Morton G. J, Stearns W. H, Rhodes C. J, Myers M. G, Jr, et al. Intracellular signalling. Key enzyme in leptin-induced anorexia. Nature. 2001;413:794–795. - PubMed
-
- Bruning J. C, Gautam D, Burks D. J, Gillette J, Schubert M, et al. Role of brain insulin receptor in control of body weight and reproduction. Science. 2000;289:2122–2125. - PubMed
-
- De Souza C. T, Araujo E. P, Bordin S, Ashimine R, Zollner R. L, et al. Consumption of a fat-rich diet activates a proinflammatory response and induces insulin resistance in the hypothalamus. Endocrinology. 2005;146:4192–4199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

