Loss of hepatocyte-nuclear-factor-1alpha impacts on adult mouse intestinal epithelial cell growth and cell lineages differentiation
- PMID: 20808783
- PMCID: PMC2927538
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012378
Loss of hepatocyte-nuclear-factor-1alpha impacts on adult mouse intestinal epithelial cell growth and cell lineages differentiation
Abstract
Background and aims: Although Hnf1alpha is crucial for pancreas and liver functions, it is believed to play a limited functional role for intestinal epithelial functions. The aim of this study was to assess the consequences of abrogating Hnf1alpha on the maintenance of adult small intestinal epithelial functions.
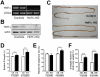
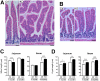
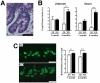
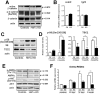
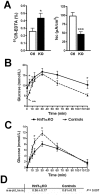
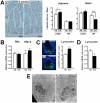
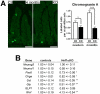
Methodology/principal findings: An Hnf1alpha knockout mouse model was used. Assessment of histological abnormalities, crypt epithelial cell proliferation, epithelial barrier, glucose transport and signalling pathways were measured in these animals. Changes in global gene expression were also analyzed. Mice lacking Hnf1alpha displayed increased crypt proliferation and intestinalomegaly as well as a disturbance of intestinal epithelial cell lineages production during adult life. This phenotype was associated with a decrease of the mucosal barrier function and lumen-to-blood glucose delivery. The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signalling pathway was found to be overly activated in the small intestine of adult Hnf1alpha mutant mice. The intestinal epithelium of Hnf1alpha null mice displayed a reduction of the enteroendocrine cell population. An impact was also observed on proper Paneth cell differentiation with abnormalities in the granule exocytosis pathway.
Conclusions/significance: Together, these results unravel a functional role for Hnf1alpha in regulating adult intestinal growth and sustaining the functions of intestinal epithelial cell lineages.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
mTOR disruption causes intestinal epithelial cell defects and intestinal atrophy postinjury in mice.FASEB J. 2016 Mar;30(3):1263-75. doi: 10.1096/fj.15-278606. Epub 2015 Nov 30. FASEB J. 2016. PMID: 26631481 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperation between HNF-1alpha, Cdx2, and GATA-4 in initiating an enterocytic differentiation program in a normal human intestinal epithelial progenitor cell line.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010 Apr;298(4):G504-17. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00265.2009. Epub 2010 Feb 4. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20133952 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1alpha and beta control terminal differentiation and cell fate commitment in the gut epithelium.Development. 2010 May;137(9):1573-82. doi: 10.1242/dev.044420. Development. 2010. PMID: 20388655
-
Paneth Cells: Dispensable yet Irreplaceable for the Intestinal Stem Cell Niche.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025;19(4):101443. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2024.101443. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 39708920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucose and amino acid in enterocyte: absorption, metabolism and maturation.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2018 Mar 1;23(9):1721-1739. doi: 10.2741/4669. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2018. PMID: 29293459 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor-4α regulates expression of the serotonin transporter in intestinal epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020 Jun 1;318(6):C1294-C1304. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00477.2019. Epub 2020 Apr 29. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32348179 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating ghrelin level is higher in HNF1A-MODY and GCK-MODY than in polygenic forms of diabetes mellitus.Endocrine. 2015 Dec;50(3):643-9. doi: 10.1007/s12020-015-0627-5. Epub 2015 May 19. Endocrine. 2015. PMID: 25987348 Free PMC article.
-
The Hippo Pathway Effector YAP1 Regulates Intestinal Epithelial Cell Differentiation.Cells. 2020 Aug 13;9(8):1895. doi: 10.3390/cells9081895. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32823612 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant protein Schistosoma japonicum-derived molecule attenuates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis by inhibiting miRNA-217-5p to alleviate apoptosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Dec 14;27(46):7982-7994. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i46.7982. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 35046625 Free PMC article.
-
HNF1α defect influences post-prandial lipid regulation.PLoS One. 2017 May 11;12(5):e0177110. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177110. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28493909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crosnier C, Stamataki D, Lewis J. Organizing cell renewal in the intestine: stem cells, signals and combinatorial control. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:349–359. - PubMed
-
- Scoville DH, Sato T, He XC, Li L. Current view: intestinal stem cells and signaling. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:849–864. - PubMed
-
- Traber PG, Wu GD. Rustgi AK, editor. Intestinal Development and Differentiation. Gastrointestinal Cancers: Biology, Diagnosis, and Therapy Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven Publishers. 1995. pp. 21–43.
-
- Menard D, Beaulieu JF, Boudreau F, Perreault N, Rivard N, et al. Unsicker K, Krieglstein K, editors. Gastrointestinal tract. Cell signaling and growth factors in development: from molecules to organogenesis: Wiley-VCH. 2006. pp. 755–790.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

