Distinct changes in cAMP and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase signalling in L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia
- PMID: 20808799
- PMCID: PMC2925943
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012322
Distinct changes in cAMP and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase signalling in L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia
Abstract
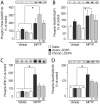
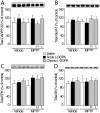
Background: In rodents, the development of dyskinesia produced by L-DOPA in the dopamine-depleted striatum occurs in response to increased dopamine D1 receptor-mediated activation of the cAMP - protein kinase A and of the Ras-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signalling pathways. However, very little is known, in non-human primates, about the regulation of these signalling cascades and their association with the induction, manifestation and/or maintenance of dyskinesia.
Methodology/results: We here studied, in the gold-standard non-human primate model of Parkinson's disease, the changes in PKA-dependent phosphorylation of DARPP-32 and GluR1 AMPA receptor, as well as in ERK and ribosomal protein S6 (S6) phosphorylation, associated to acute and chronic administration of L-DOPA. Increased phosphorylation of DARPP-32 and GluR1 was observed in both L-DOPA first-ever exposed and chronically-treated dyskinetic parkinsonian monkeys. In contrast, phosphorylation of ERK and S6 was enhanced preferentially after acute L-DOPA administration and decreased during the course of chronic treatment.
Conclusion: Dysregulation of cAMP signalling is maintained during the course of chronic L-DOPA administration, while abnormal ERK signalling peaks during the initial phase of L-DOPA treatment and decreases following prolonged exposure. While cAMP signalling enhancement is associated with dyskinesia, abnormal ERK signalling is associated with priming.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Cotzias GC, Papavasiliou PS, Gellene R. Modification of Parkinsonism–chronic treatment with L-dopa. N Engl J Med. 1969;280:337–345. - PubMed
-
- Jenner P. Molecular mechanisms of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008;9:665–677. - PubMed
-
- Aubert I, Guigoni C, Hakansson K, Qin L, Dovero S, et al. Increased D1 dopamine receptor signalling in levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Ann Neurol. 2005;57:17–26. - PubMed
-
- Picconi B, Centonze D, Hakansson K, Bernardi G, Greengard P, et al. Loss of bidirectional striatal synaptic plasticity in L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6:501–506. - PubMed
-
- Pavon N, Martin AB, Mendialdua A, Moratalla R. ERK phosphorylation and FosB expression are associated with L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in hemiparkinsonian mice. Biol Psychiatry. 2006;59:64–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

