Optimizing combination therapies with existing and future CML drugs
- PMID: 20808800
- PMCID: PMC2925944
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012300
Optimizing combination therapies with existing and future CML drugs
Abstract
Small-molecule inhibitors imatinib, dasatinib and nilotinib have been developed to treat Chromic Myeloid Leukemia (CML). The existence of a triple-cross-resistant mutation, T315I, has been a challenging problem, which can be overcome by finding new inhibitors. Many new compounds active against T315I mutants are now at different stages of development. In this paper we develop an algorithm which can weigh different combination treatment protocols according to their cross-resistance properties, and find the protocols with the highest probability of treatment success. This algorithm also takes into account drug toxicity by minimizing the number of drugs used, and their concentration. Although our methodology is based on a stochastic model of CML microevolution, the algorithm itself does not require measurements of any parameters (such as mutation rates, or division/death rates of cells), and can be used by medical professionals without a mathematical background. For illustration, we apply this algorithm to the mutation data obtained in [1], [2].
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
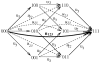
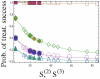
 ), diamonds (
), diamonds (
 ), triangles (
), triangles ( ). Empty markers denote three-drug treatments, and solid ones – two-drug treatments. The data are presented in tables 5 and 6.
). Empty markers denote three-drug treatments, and solid ones – two-drug treatments. The data are presented in tables 5 and 6.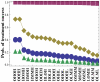
Similar articles
-
Discovery of a highly potent kinase inhibitor capable of overcoming multiple imatinib-resistant ABL mutants for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 15;897:173944. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.173944. Epub 2021 Feb 11. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33581133
-
Prevalence of BCR-ABL T315I Mutation in Malaysian Patients with Imatinib-Resistant Chronic Myeloid Leukemia.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018 Dec 25;19(12):3317-3320. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2018.19.12.3317. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018. PMID: 30583336 Free PMC article.
-
The novel anticancer agent JNJ-26854165 is active in chronic myeloid leukemic cells with unmutated BCR/ABL and T315I mutant BCR/ABL through promoting proteosomal degradation of BCR/ABL proteins.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 31;8(5):7777-7790. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13951. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27999193 Free PMC article.
-
New Bcr-Abl inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia: keeping resistance in check.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008 Jun;17(6):865-78. doi: 10.1517/13543784.17.6.865. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008. PMID: 18491988 Review.
-
Targeted chronic myeloid leukemia therapy: Seeking a cure.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007 Dec 15;64(24 Suppl 15):S9-15. doi: 10.2146/ajhp070482. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007. PMID: 18056932 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioactivity in Rhododendron: A Systemic Analysis of Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activities and Their Phylogenetic and Phytochemical Origins.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Apr 13;8:551. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00551. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28450876 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer: calculated treatment.Nature. 2013 Jul 18;499(7458):291-2. doi: 10.1038/499291a. Nature. 2013. PMID: 23868257 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging Hypoxia-Activated Prodrugs to Prevent Drug Resistance in Solid Tumors.PLoS Comput Biol. 2016 Aug 25;12(8):e1005077. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005077. eCollection 2016 Aug. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016. PMID: 27560187 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative modeling of chronic myeloid leukemia: insights from radiobiology.Blood. 2012 May 10;119(19):4363-71. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-09-381855. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22353999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamics of resistance development to imatinib under increasing selection pressure: a combination of mathematical models and in vitro data.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28955. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028955. Epub 2011 Dec 22. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22216147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calabretta B, Perrotti D. The biology of CML blast crisis. Blood. 2004;103:4010–22. - PubMed
-
- Melo JV, Hughes TP, Apperley JF. Chronic myeloid leukemia. Hematology (Am Soc Hematol Educ Program) 2003:132–52. - PubMed
-
- Shet AS, Jahagirdar BN, Verfaillie CM. Chronic myelogenous leukemia: mechanisms underlying disease progression. Leukemia. 2002;16:1402–11. - PubMed

