Lymphocytes accelerate epithelial tight junction assembly: role of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)
- PMID: 20808811
- PMCID: PMC2925955
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012343
Lymphocytes accelerate epithelial tight junction assembly: role of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)
Abstract
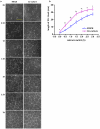
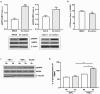
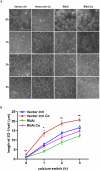
The tight junctions (TJs), characteristically located at the apicolateral borders of adjacent epithelial cells, are required for the proper formation of epithelial cell polarity as well as for sustaining the mucosal barrier to the external environment. The observation that lymphocytes are recruited by epithelial cells to the sites of infection [1] suggests that they may play a role in the modulation of epithelial barrier function and thus contribute to host defense. To test the ability of lymphocytes to modulate tight junction assembly in epithelial cells, we set up a lymphocyte-epithelial cell co-culture system, in which Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells, a well-established model cell line for studying epithelial TJ assembly [2], were co-cultured with mouse lymphocytes to mimic an infection state. In a typical calcium switch experiment, the TJ assembly in co-culture was found to be accelerated compared to that in MDCK cells alone. This accelaration was found to be mediated by AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK activation was independent of changes in cellular ATP levels but it was found to be activated by the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-alpha. Forced suppression of AMPK, either with a chemical inhibitor or by knockdown, abrogated the accelerating effect of lymphocytes on TJ formation. Similar results were also observed in a co-culture with lymphocytes and Calu-3 human airway epithelial cells, suggesting that the activation of AMPK may be a general mechanism underlying lymphocyte-accelerated TJ assembly in different epithelia. These results suggest that signals from lymphocytes, such as cytokines, facilitate TJ assembly in epithelial cells via the activation of AMPK.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Implications of AMPK in the Formation of Epithelial Tight Junctions.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jul 13;19(7):2040. doi: 10.3390/ijms19072040. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30011834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of epithelial tight junction assembly and disassembly by AMP-activated protein kinase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jan 16;104(3):819-22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0610157104. Epub 2007 Jan 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17204563 Free PMC article.
-
AMP-activated protein kinase regulates the assembly of epithelial tight junctions.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Nov 14;103(46):17272-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608531103. Epub 2006 Nov 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17088526 Free PMC article.
-
Butyrate enhances the intestinal barrier by facilitating tight junction assembly via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in Caco-2 cell monolayers.J Nutr. 2009 Sep;139(9):1619-25. doi: 10.3945/jn.109.104638. Epub 2009 Jul 22. J Nutr. 2009. PMID: 19625695 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal Association between the Apical Junctional Complex and AMPK: A Promising Therapeutic Target for Epithelial/Endothelial Barrier Function?Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 29;20(23):6012. doi: 10.3390/ijms20236012. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31795328 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Direct Action of Non-Digestible Oligosaccharides against a Leaky Gut.Nutrients. 2022 Nov 7;14(21):4699. doi: 10.3390/nu14214699. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36364961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LPS Stimulation Induces Small Heterodimer Partner Expression Through the AMPK-NRF2 Pathway in Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea).Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 8;12:753681. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.753681. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34819934 Free PMC article.
-
Necrotic Enteritis in Broiler Chickens: The Role of Tight Junctions and Mucosal Immune Responses in Alleviating the Effect of the Disease.Microorganisms. 2019 Jul 31;7(8):231. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7080231. Microorganisms. 2019. PMID: 31370350 Free PMC article.
-
Fyn phosphorylates AMPK to inhibit AMPK activity and AMP-dependent activation of autophagy.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 15;7(46):74612-74629. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11916. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27626315 Free PMC article.
-
Necrotic Enteritis in Broiler Chickens: A Review on the Pathogen, Pathogenesis, and Prevention.Microorganisms. 2022 Sep 30;10(10):1958. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10101958. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36296234 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Robbins RA, Shoji S, Linder J, Gossman GL, Allington LA, et al. Bronchial epithelial cells release chemotactic activity for lymphocytes. Am J Physiol. 1989;257:L109–115. - PubMed
-
- Herard AL, Zahm JM, Pierrot D, Hinnrasky J, Fuchey C, et al. Epithelial barrier integrity during in vitro wound repair of the airway epithelium. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1996;15:624–632. - PubMed
-
- Denker BM, Nigam SK. Molecular structure and assembly of the tight junction. Am J Physiol. 1998;274:F1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

