Novel association strategy with copy number variation for identifying new risk Loci of human diseases
- PMID: 20808825
- PMCID: PMC2924882
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012185
Novel association strategy with copy number variation for identifying new risk Loci of human diseases
Abstract
Background: Copy number variations (CNV) are important causal genetic variations for human disease; however, the lack of a statistical model has impeded the systematic testing of CNVs associated with disease in large-scale cohort.
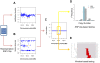
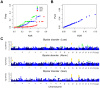
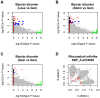
Methodology/principal findings: Here, we developed a novel integrated strategy to test CNV-association in genome-wide case-control studies. We converted the single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) signal to copy number states using a well-trained hidden Markov model. We mapped the susceptible CNV-loci through SNP site-specific testing to cope with the physiological complexity of CNVs. We also ensured the credibility of the associated CNVs through further window-based CNV-pattern clustering. Genome-wide data with seven diseases were used to test our strategy and, in total, we identified 36 new susceptible loci that are associated with CNVs for the seven diseases: 5 with bipolar disorder, 4 with coronary artery disease, 1 with Crohn's disease, 7 with hypertension, 9 with rheumatoid arthritis, 7 with type 1 diabetes and 3 with type 2 diabetes. Fifteen of these identified loci were validated through genotype-association and physiological function from previous studies, which provide further confidence for our results. Notably, the genes associated with bipolar disorder converged in the phosphoinositide/calcium signaling, a well-known affected pathway in bipolar disorder, which further supports that CNVs have impact on bipolar disorder.
Conclusions/significance: Our results demonstrated the effectiveness and robustness of our CNV-association analysis and provided an alternative avenue for discovering new associated loci of human diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of copy number variation in susceptibility to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: genome-wide association study and comparison with published loci.PLoS One. 2009 Dec 4;4(12):e8175. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008175. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19997636 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association and targeted analysis of copy number variants with psoriatic arthritis in German patients.BMC Med Genet. 2017 Aug 23;18(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12881-017-0447-y. BMC Med Genet. 2017. PMID: 28835222 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Intellectual Disability Copy Number Variants for Association With Schizophrenia.JAMA Psychiatry. 2016 Sep 1;73(9):963-969. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2016.1831. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27602560 Free PMC article.
-
Extending genome-wide association studies to copy-number variation.Hum Mol Genet. 2008 Oct 15;17(R2):R135-42. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddn282. Hum Mol Genet. 2008. PMID: 18852202 Review.
-
Clinical significance of germline copy number variation in susceptibility of human diseases.J Genet Genomics. 2018 Jan 20;45(1):3-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2018.01.001. Epub 2018 Jan 5. J Genet Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29396143 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic structural variations for cardiovascular and metabolic comorbidity.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 25;7:41268. doi: 10.1038/srep41268. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28120895 Free PMC article.
-
From the Eukaryotic Molybdenum Cofactor Biosynthesis to the Moonlighting Enzyme mARC.Molecules. 2018 Dec 11;23(12):3287. doi: 10.3390/molecules23123287. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30545001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rare genomic structural variants in complex disease: lessons from the replication of associations with obesity.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58048. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058048. Epub 2013 Mar 12. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23554873 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Genome-wide association study of copy number variation with lung function identifies a novel signal of association near BANP for forced vital capacity.BMC Genet. 2016 Aug 11;17(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s12863-016-0423-0. BMC Genet. 2016. PMID: 27514831 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of genomics on pediatric research and medicine.Pediatrics. 2012 Jun;129(6):1150-60. doi: 10.1542/peds.2011-3636. Epub 2012 May 7. Pediatrics. 2012. PMID: 22566424 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gonzalez E, Kulkarni H, Bolivar H, Mangano A, Sanchez R, et al. The influence of CCL3L1 gene-containing segmental duplications on HIV-1/AIDS susceptibility. Science. 2005;307:1434–1440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

