Examination of apoptosis signaling in pancreatic cancer by computational signal transduction analysis
- PMID: 20808857
- PMCID: PMC2924379
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012243
Examination of apoptosis signaling in pancreatic cancer by computational signal transduction analysis
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remains an important cause of cancer death. Changes in apoptosis signaling in pancreatic cancer result in chemotherapy resistance and aggressive growth and metastasizing. The aim of this study was to characterize the apoptosis pathway in pancreatic cancer computationally by evaluation of experimental data from high-throughput technologies and public data bases. Therefore, gene expression analysis of microdissected pancreatic tumor tissue was implemented in a model of the apoptosis pathway obtained by computational protein interaction prediction.
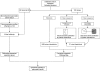
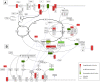
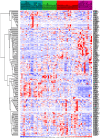
Methodology/principal findings: Apoptosis pathway related genes were assembled from electronic databases. To assess expression of these genes we constructed a virtual subarray from a whole genome analysis from microdissected native tumor tissue. To obtain a model of the apoptosis pathway, interactions of members of the apoptosis pathway were analysed using public databases and computational prediction of protein interactions. Gene expression data were implemented in the apoptosis pathway model. 19 genes were found differentially expressed and 12 genes had an already known pathophysiological role in PDAC, such as Survivin/BIRC5, BNIP3 and TNF-R1. Furthermore we validated differential expression of IL1R2 and Livin/BIRC7 by RT-PCR and immunohistochemistry. Implementation of the gene expression data in the apoptosis pathway map suggested two higher level defects of the pathway at the level of cell death receptors and within the intrinsic signaling cascade consistent with references on apoptosis in PDAC. Protein interaction prediction further showed possible new interactions between the single pathway members, which demonstrate the complexity of the apoptosis pathway.
Conclusions/significance: Our data shows that by computational evaluation of public accessible data an acceptable virtual image of the apoptosis pathway might be given. By this approach we could identify two higher level defects of the apoptosis pathway in PDAC. We could further for the first time identify IL1R2 as possible candidate gene in PDAC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Integrative analysis of gene expression profiles reveals specific signaling pathways associated with pancreatic duct adenocarcinoma.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2018 Apr 27;38(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s40880-018-0289-9. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2018. PMID: 29764514 Free PMC article.
-
Microarray analysis of gene expression profile of multidrug resistance in pancreatic cancer.Chin Med J (Engl). 2007 Oct 20;120(20):1743-52. Chin Med J (Engl). 2007. PMID: 18028764
-
Analysis of molecular pathways in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas with a bioinformatics approach.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(6):2561-7. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.6.2561. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015. PMID: 25824797
-
Gene expression profiling of microdissected pancreatic ductal carcinomas using high-density DNA microarrays.Neoplasia. 2004 Sep-Oct;6(5):611-22. doi: 10.1593/neo.04295. Neoplasia. 2004. PMID: 15548371 Free PMC article.
-
Confirmation of DNA microarray-derived differentially expressed genes in pancreatic cancer using quantitative RT-PCR.Pancreatology. 2009;9(5):577-82. doi: 10.1159/000212084. Epub 2009 Aug 4. Pancreatology. 2009. PMID: 19657213 Review.
Cited by
-
WikiPathways: building research communities on biological pathways.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jan;40(Database issue):D1301-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1074. Epub 2011 Nov 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22096230 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous profiling of 194 distinct receptor transcripts in human cells.Sci Signal. 2013 Aug 6;6(287):rs13. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2003624. Sci Signal. 2013. PMID: 23921087 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of MUC1 Induces Non-Canonical TGF-β Signaling in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 14;10:821875. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.821875. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35237602 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic determinants of cardiovascular events among women with migraine: a genome-wide association study.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22106. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022106. Epub 2011 Jul 14. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21779381 Free PMC article.
-
Decoys and Regulatory "Receptors" of the IL-1/Toll-Like Receptor Superfamily.Front Immunol. 2013 Jul 9;4:180. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00180. eCollection 2013. Front Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23847621 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, et al. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–249. - PubMed
-
- Lowenfels AB, Maisonneuve P. Epidemiology and risk factors for pancreatic cancer. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2006;20:197–209. - PubMed
-
- Wolff RA, Chiao P, Lenzi R, Pisters PW, Lee JE, et al. Current approaches and future strategies for pancreatic carcinoma. Invest New Drugs. 2000;18:43–56. - PubMed
-
- Brown JM, Attardi LD. The role of apoptosis in cancer development and treatment response. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:231–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

