Diurnal variation in urodynamics of rat
- PMID: 20808873
- PMCID: PMC2924395
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012298
Diurnal variation in urodynamics of rat
Abstract
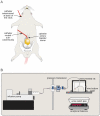
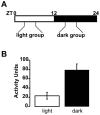
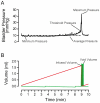
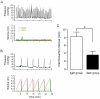
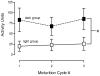
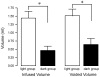
In humans, the storage and voiding functions of the urinary bladder have a characteristic diurnal variation, with increased voiding during the day and urine storage during the night. However, in animal models, the daily functional differences in urodynamics have not been well-studied. The goal of this study was to identify key urodynamic parameters that vary between day and night. Rats were chronically instrumented with an intravesical catheter, and bladder pressure, voided volumes, and micturition frequency were measured by continuous filling cystometry during the light (inactive) or dark (active) phases of the circadian cycle. Cage activity was recorded by video during the experiment. We hypothesized that nocturnal rats entrained to a standard 12:12 light:dark cycle would show greater ambulatory activity and more frequent, smaller volume micturitions in the dark compared to the light. Rats studied during the light phase had a bladder capacity of 1.44+/-0.21 mL and voided every 8.2+/-1.2 min. Ambulatory activity was lower in the light phase, and rats slept during the recording period, awakening only to urinate. In contrast, rats studied during the dark were more active, had a lower bladder capacities (0.65+/-0.18 mL), and urinated more often (every 3.7+/-0.9 min). Average bladder pressures were not significantly different between the light and dark (13.40+/-2.49 and 12.19+/-2.85 mmHg, respectively). These results identify a day-night difference in bladder capacity and micturition frequency in chronically-instrumented nocturnal rodents that is phase-locked to the normal circadian locomotor activity rhythm of the animal. Furthermore, since it has generally been assumed that the daily hormonal regulation of renal function is a major driver of the circadian rhythm in urination, and few studies have addressed the involvement of the lower urinary tract, these results establish the bladder itself as a target for circadian regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chronobiology of micturition: putative role of the circadian clock.J Urol. 2013 Sep;190(3):843-9. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.02.024. Epub 2013 Feb 18. J Urol. 2013. PMID: 23429068 Review.
-
Urodynamic patterns of normal male micturition: influence of water consumption on urine production and detrusor function.J Urol. 2002 Oct;168(4 Pt 1):1458-63. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)64473-4. J Urol. 2002. PMID: 12352417
-
Urodynamic measurements reflect physiological bladder function in rats.Neurourol Urodyn. 2018 Apr;37(4):1266-1271. doi: 10.1002/nau.23455. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Neurourol Urodyn. 2018. PMID: 29140562
-
Reduction in nocturnal functional bladder capacity is a common factor in the pathogenesis of refractory nocturnal enuresis.BJU Int. 2002 Aug;90(3):302-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.2002.02884.x. BJU Int. 2002. PMID: 12133069
-
[Recommendations for the urodynamic examination in the investigation of non-neurological female urinary incontinence].Prog Urol. 2007 Nov;17(6 Suppl 2):1264-84. Prog Urol. 2007. PMID: 18214138 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Glucocorticoids coordinate the bladder peripheral clock and diurnal micturition pattern in mice.Commun Biol. 2023 Jan 21;6(1):81. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-04464-3. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 36681730 Free PMC article.
-
Local receptors as novel regulators for peripheral clock expression.FASEB J. 2014 Nov;28(11):4610-6. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-243295. Epub 2014 Aug 21. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 25145629 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Isoflavone-Rich NADES Extract of Pueraria lobata Roots and Astaxanthin-Rich Phaffia rhodozyma Extract on Prostate Carcinogenesis in Rats.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 26;12(3):564. doi: 10.3390/plants12030564. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36771648 Free PMC article.
-
Cystometric and External Urethral Sphincter Measurements in Awake Rats with Implanted Catheter and Electrodes Allowing for Repeated Measurements.J Vis Exp. 2018 Jan 30;(131):56506. doi: 10.3791/56506. J Vis Exp. 2018. PMID: 29443095 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Electroacupuncture on Bladder Dysfunction via Regulation of MLC and MLCK Phosphorylation in a Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Jun 10;2021:5558890. doi: 10.1155/2021/5558890. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34221075 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reppert SM, Weaver DR. Coordination of circadian timing in mammals. Nature. 2002;418:935–941. - PubMed
-
- Van Hoeck K, Bael A, Lax H, Hirche H, van Gool JD. Circadian variation of voided volume in normal school-age children. Eur J Pediatr. 2007;166:579–584. - PubMed
-
- Ku JH, Lim DJ, Byun SS, Paick JS, Oh SJ. Nocturia in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms: association with diurnal voiding patterns. BJU Int. 2004;93:1005–1008. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

