Small molecule inhibitors of DNA repair nuclease activities of APE1
- PMID: 20809131
- PMCID: PMC2956791
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-010-0488-2
Small molecule inhibitors of DNA repair nuclease activities of APE1
Abstract
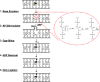
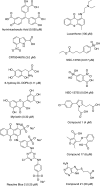
APE1 is a multifunctional protein that possesses several nuclease activities, including the ability to incise at apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) sites in DNA or RNA, to excise 3'-blocking termini from DNA ends, and to cleave at certain oxidized base lesions in DNA. Pre-clinical and clinical data indicate a role for APE1 in the pathogenesis of cancer and in resistance to DNA-interactive drugs, particularly monofunctional alkylators and antimetabolites. In an effort to improve the efficacy of therapeutic compounds, such as temozolomide, groups have begun to develop high-throughput screening assays and to identify small molecule inhibitors against APE1 repair nuclease activities. It is envisioned that such inhibitors will be used in combinatorial treatment paradigms to enhance the efficacy of DNA-interactive drugs that introduce relevant cytotoxic DNA lesions. In this review, we summarize the current state of the efforts to design potent and selective inhibitors against APE1 AP site incision activity.
Figures



References
-
- Friedberg EC. A brief history of the DNA repair field. Cell Res. 2008;18:3–7. - PubMed
-
- Dulbecco R. Reactivation of ultra-violet-inactivated bacteriophage by visible light. Nature. 1949;163:949. - PubMed
-
- Rupert CS. Enzymatic photoreactivation: overview. Basic Life Sci. 1975;5A:73–87. - PubMed
-
- Lindahl T. Instability and decay of the primary structure of DNA. Nature. 1993;362:709–715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

