Biochemistry of the anterior, medial, and posterior genioglossus in the aged rat
- PMID: 20809174
- PMCID: PMC2998581
- DOI: 10.1007/s00455-010-9297-x
Biochemistry of the anterior, medial, and posterior genioglossus in the aged rat
Abstract
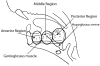
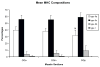
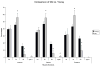
Age-related tongue weakness may contribute to swallowing deficits in the elderly. One contributing factor may be an alteration in muscle-fiber-type properties with aging. However, it is not clear how muscle fiber types within the aged tongue may vary from those found in young adults, or how fiber types may vary across the anteroposterior axis of the extrinsic tongue muscles. We examined the myosin heavy chain (MHC) composition of anterior, medial, and posterior sections of the genioglossus muscle (GG) in ten old male Fischer 344/Brown Norway rats and compared findings to previously reported data from young adult male rats. Significant differences (p < 0.01) between young adult and old rats were found in the distribution of MHC isoforms along the anteroposterior axis of the muscle. In the anterior, medial, and posterior regions, there was a significantly smaller proportion of type IIb MHC in the old rat GG muscles, while the proportion of type IIx MHC was significantly greater. In the medial region, the proportion of type I MHC was found to be significantly greater in the old rats. Thus, we found a shift to more slowly contracting muscle fibers in the aged rat tongue.
Figures
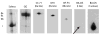

References
-
- Miller AJ. The neurobiology of swallowing and dysphagia. Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2008;14(2):77–86. - PubMed
-
- Doherty TJ, Brown WF. Age-related changes in the twitch contractile properties of human thenar motor units. J Appl Physiol. 1997;82(1):93–101. - PubMed
-
- Doherty TJ. Invited review: Aging and sarcopenia. J Appl Physiol. 2003;95(4):1717–1727. - PubMed
-
- Brooks SV, Faulkner JA. Skeletal muscle weakness in old age: Underlying mechanisms. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 1994;26(4):432–439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

