Viral DNA contamination is responsible for Epstein-Barr virus detection in cytotoxic T lymphocytes stimulated in vitro with Epstein-Barr virus B-lymphoblastoid cell line
- PMID: 20809356
- PMCID: PMC11030803
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-010-0913-2
Viral DNA contamination is responsible for Epstein-Barr virus detection in cytotoxic T lymphocytes stimulated in vitro with Epstein-Barr virus B-lymphoblastoid cell line
Abstract
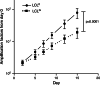
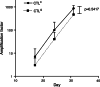
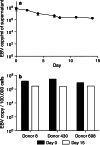
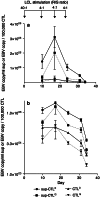
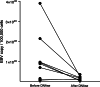
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-transformed B-lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) are used to prepare human EBV-specific T lymphocytes (EBV-CTL) in vitro. Within an LCL, up to 5-7% the cells release infectious EBV, and this has fostered safety concerns for therapeutic applications because of the exposure of T cells to EBV. The release of infectious viruses can be prevented by ganciclovir, but this drug may seriously affect LCL growth. In the wake of these concerns, the present work was designed to compile safety data on EBV-CTL preparation for the purpose of submission to a regulatory agency. We showed that further to supernatant exclusion, the number of EBV genome copies (EBVc) associated with the EBV-CTL always made up a constant proportion of the EBVc number detected in the culture supernatant. In addition, such was the case whether infectious virus could be produced by the LCL or not, suggesting that the EBV signal detected was due to a DNA contamination rather than an infection. Furthermore, we demonstrated that the number of EBVc associated with the EBV-CTL was highly sensitive to DNAse treatment, and finally that EBVc could no longer be detected after the EBV-CTL had been amplified in the absence of LCL. Consequently, during in vitro EBV-CTL preparation, either T cells cannot be infected or they die rapidly after EBV infection.
Figures
References
-
- Walter EA, Greenberg PD, Gilbert MJ, Finch RJ, Watanabe KS, Thomas ED, Riddell SR. Reconstitution of cellular immunity against cytomegalovirus in recipients of allogeneic bone marrow by transfer of T-cell clones from the donor. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1038–1044. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199510193331603. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Haque T, Amlot PL, Helling N, Thomas JA, Sweny P, Rolles K, Burroughs AK, Prentice HG, Crawford DH. Reconstitution of EBV-specific T cell immunity in solid organ transplant recipients. J Immunol. 1998;160:6204–6209. - PubMed
-
- Heslop H, Rooney C, Brenner M, Krance R, Carrum G, Gahn B, Bollard C, Khan S, Gee A, Popat U, et al. Administration of neomycin resistance gene-marked EBV-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes as therapy for patients receiving a bone marrow transplant for relapsed EBV-positive Hodgkin disease. Hum Gene Ther. 2000;11:1465–1475. doi: 10.1089/10430340050057530. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lucas KG, Sun Q, Burton RL, Tilden A, Vaughan WP, Carabasi M, Salzman D, Ship A. A phase I-II trial to examine the toxicity of CMV- and EBV-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes when used for prophylaxis against EBV and CMV disease in recipients of CD34-selected/T cell-depleted stem cell transplants. Hum Gene Ther. 2000;11:1453–1463. doi: 10.1089/10430340050057521. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

