Multidirectional time-dependent effect of sinigrin and allyl isothiocyanate on metabolic parameters in rats
- PMID: 20809411
- PMCID: PMC2944953
- DOI: 10.1007/s11130-010-0183-3
Multidirectional time-dependent effect of sinigrin and allyl isothiocyanate on metabolic parameters in rats
Abstract
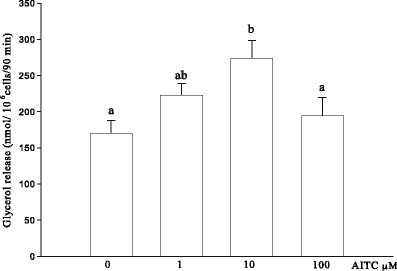
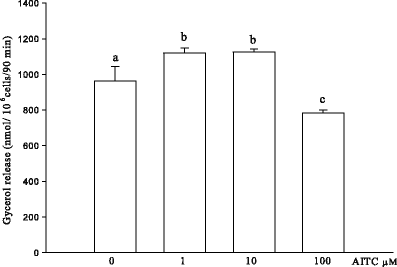
Sinigrin (SIN) and allyl isothiocyanate (AITC) are compounds found in high concentrations in Brassica family vegetables, especially in Brussels sprouts. Recently, they have been used as a nutrition supplement for their preventive and medicinal effect on some types of cancer and other diseases. In this research, nutritional significance of parent glucosinolate sinigrin 50 μmol/kg b. w./day and its degradation product allyl isothiocyanate 25 μmol/kg b. w./day and 50 μmol/kg b. w./day was studied by the evaluation of their influence on some parameters of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in an animal rat model in vivo after their single (4 h) and 2 weeks oral administration. Additionally, the aim of this trial was to evaluate the direct action of AITC on basal and epinephrine-induced lipolysis in isolated rat adipocytes at concentration 1 μM, 10 μM and 100 μM in vitro. Sole AITC after 4 h of its ingestion caused liver triacylglycerols increment at both doses and glycaemia only at the higher dose. Multiple SIN treatment showed its putative bioconversion into AITC. It was found that SIN and AITC multiple administration in the same way strongly disturbed lipid and carbohydrate homeostasis, increasing esterified and total cholesterol, free fatty acids and lowering tracylglycerols in the blood serum. Additionally, AITC at both doses elevated insulinaemia and liver glycogen enhancement. The in vitro experiment revealed that AITC potentiated basal lipolysis process at 10 μM, and had stimulatory effect on epinephrine action at 1 μM and 10 μM. The results of this study demonstrated that the effect of SIN and AITC is multidirectional, indicating its impact on many organs like liver as well as pancreas, intestine in vivo action and rat adipocytes in vitro. Whilst consumption of cruciferous vegetables at levels currently considered "normal" seems to be beneficial to human health, this data suggest that any large increase in intake could conceivably lead to undesirable effect. This effect is potentiated with time of action of the examined compounds, whose influence is rather adverse for the majority of metabolic pathways (liver steatosis at short duration and insulinaemia, cholesterolaemia at long time treatment). Beneficial action of AITC concerned intensified hydrolysis of TG in the blood serum with a simultaneous lipolysis in adipocytes.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

