Chondroitinase ABC enhances pericontusion axonal sprouting but does not confer robust improvements in behavioral recovery
- PMID: 20809786
- PMCID: PMC2978059
- DOI: 10.1089/neu.2010.1470
Chondroitinase ABC enhances pericontusion axonal sprouting but does not confer robust improvements in behavioral recovery
Abstract
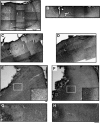
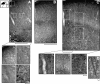
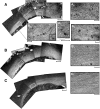
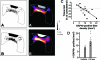
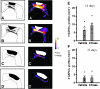
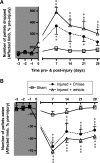
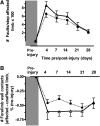
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) results in enduring functional deficits. Strategies aimed at promoting plasticity within the injured brain may aid in enhancing functional outcome. We have previously shown that spontaneous pericontusional axon sprouting occurs within 7-14 days after controlled cortical impact injury in the adult rat, but ultimately fails due to an increasingly growth-inhibitory environment. We therefore sought to determine whether acute infusion of chondroitinase ABC into the site of the cortical contusion, to further reduce pericontusional growth-inhibitory chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPGs), would enhance and prolong the sprouting response. We also wanted to determine if chondroitinase-enhanced sprouting would ameliorate the behavioral deficits in forelimb function that occur in this model. Acute chondroitinase infusion decreased intact CSPGs and significantly increased pericontusional cortical grey and white matter growth-associated protein 43 (GAP43)-positive axon sprouting at 7 days post-injury. A return of intact CSPGs at later time points likely contributed to the absence of persistently increased levels of axon sprouting by 14-21 days post-injury. There was no overall benefit on forelimb function during the time of maximal sprouting or at any subsequent times in three of four behavioral outcome measures. However, there was a chondroitinase-induced improvement in recovery from unskilled limb use deficits on the staircase forelimb reaching test toward sham-injured values at 28 days, which was not achieved by the vehicle-treated rats, indicating that there is some minor functional benefit of the increased sprouting induced by chondroitinase treatment. The current results, together with data from spinal cord injury models after chondroitinase intervention, suggest that a combinatorial approach with the addition of neurotrophins and rehabilitation would result in more robust axon sprouting and consequently improve behavioral outcome.
Figures
References
-
- Baker A.J. Phan N. Moulton R.J. Fehlings M.G. Yucel Y. Zhao M. Liu E. Tian G.F. Attenuation of the electrophysiological function of the corpus callosum after fluid percussion injury in the rat. J. Neurotrauma. 2002;19:587–599. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury E. Moon L. Popat R. King V. Bennett G. Patel P. Fawcett J. McMahon S. Chondroitinase ABC promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Nature. 2002;416:636–640. - PubMed
-
- Bruckner G. Bringmann A. Hartig W. Koppe G. Delpech B. Brauer K. Acute and long-lasting changes in extracellular-matrix chondroitin-sulphate proteoglycans induced by injection of chondroitinase ABC in the adult rat brain. Exp. Brain Res. 1998;121:300–310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

