Expression of transcription factors snail, slug, and twist in human bladder carcinoma
- PMID: 20809941
- PMCID: PMC2942802
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-9966-29-119
Expression of transcription factors snail, slug, and twist in human bladder carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Slug, snail, and twist are transcription factors that regulate the expression of tumor suppressors such as E-cadherin. In this study, we aimed to examine the expression of these transcription factors in human bladder carcinoma.
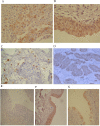
Methods: We first investigated expression of slug, snail, twist and E-cadherin in five bladder Carcinoma cell lines by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and western blotting. Furthermore, we investigated slug, snail, and twist and E-cadherin expression by immunohistochemistry with bladder carcinoma (tumor, n = 120; background, n = 42).
Results: Expression of slug mRNA and protein was detected in all cell lines, twist was clearly expressed in two out of five bladder carcinoma cell lines, snail was not expressed, and E-cadherin was detected in 3 cell lines. 44.2% (53/120) of human bladder carcinoma tissues and 38% (16/42) background tissue showed an expression of twist; 62.5% (75/120) of human bladder carcinoma tissues and 40% (17/42) background tissue showed an expression of slug, 15.8% (19/120) of human bladder carcinoma tissues and 76% (32/42) background tissue showed an expression of snail, and 25.8% (31/120) cases were negative for E-cadherin expression in carcinoma tissues. Expression of slug and twist shows increased levels in tumors, whereas snail seems reduced. Statistically significant correlations were found between twist, slug, and E-cadherin expression. Immunohistochemistry analysis showed that twist was elevated with increasing tumor stage (P = 0.001), the grade (P < 0.001), the progression (P = 0.035). Slug was elevated and snail was reduced with increasing nodal involvement (tumor-node-metastasis status) (P = 0.004, P = 0.01). E-cadherin was reduced in expression corresponding with tumor grade (P < 0.01). Positive twist, slug and E-cadherin expression clearly predicted poorer PFS (P = 0.042, P = 0.014, P = 0.001). In the multivariate analysis, only snail and E-cadherin expression were independent prognostic factors for OS (P = 0.002, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: These data demonstrate that twist, snail and slug have inappropriate expression in bladder carcinoma and that this may play a part in the progression of human bladder carcinoma.
Figures
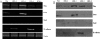
Similar articles
-
Changes in the expression of E-cadherin repressors, Snail, Slug, SIP1, and Twist, in the development and progression of ovarian carcinoma: the important role of Snail in ovarian tumorigenesis and progression.Med Mol Morphol. 2009 Jun;42(2):82-91. doi: 10.1007/s00795-008-0436-5. Epub 2009 Jun 18. Med Mol Morphol. 2009. PMID: 19536615
-
Co-expression of SNAIL and TWIST determines prognosis in estrogen receptor-positive early breast cancer patients.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 May;133(1):49-59. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1684-y. Epub 2011 Jul 28. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 21796367
-
Slug contributes to cadherin switch and malignant progression in muscle-invasive bladder cancer development.Urol Oncol. 2013 Nov;31(8):1751-60. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2012.02.001. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Urol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 22421353
-
Genetic And Epigenetic Regulation Of E-Cadherin Signaling In Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Oct 16;11:8947-8963. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S225606. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 31802937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery and characterization of a small molecule that restores E-cadherin expression in cancer cell lines via a new mechanism.2012 Dec 13 [updated 2013 Mar 22]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. 2012 Dec 13 [updated 2013 Mar 22]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. PMID: 26913352 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Elevated eukaryotic elongation factor 2 expression is involved in proliferation and invasion of lung squamous cell carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 6;7(36):58470-58482. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11298. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27542262 Free PMC article.
-
Molecules involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and epithelial-stromal interaction in phyllodes tumors: implications for histologic grade and prognosis.Tumour Biol. 2012 Jun;33(3):787-98. doi: 10.1007/s13277-011-0296-9. Epub 2011 Dec 29. Tumour Biol. 2012. PMID: 22203494
-
N1-guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane sensitizes bladder cancer cells to doxorubicin by preventing epithelial-mesenchymal transition through inhibition of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 activation.Cancer Sci. 2014 Feb;105(2):219-27. doi: 10.1111/cas.12328. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Cancer Sci. 2014. PMID: 24262005 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine-mediated immunotherapy directed against a transcription factor driving the metastatic process.Cancer Res. 2014 Apr 1;74(7):1945-57. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-2045. Epub 2014 Feb 11. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24520078 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical Study EMT-Related Proteins in HPV-, and EBV-Negative Patients with Sinonasal Tumours.Pathol Oncol Res. 2016 Oct;22(4):781-8. doi: 10.1007/s12253-016-0068-3. Epub 2016 Apr 30. Pathol Oncol Res. 2016. PMID: 27138192
References
-
- Thurman SA, De Weese TL. Multimodality therapy for the treatment of muscle-invasive bladder cancer, Semin. Urol Oncol. 2000;18:313–322. - PubMed
-
- Fondrevelle Marie E, Kantelip Bernadette, Reiter Robert E. The expression of Twist has an impact on survival in human bladder cancer and is influenced by the smoking status. Urologic Oncology. 2009;27:268–276. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

