Effectiveness of BCG vaccination to aged mice
- PMID: 20809944
- PMCID: PMC2936867
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4933-7-12
Effectiveness of BCG vaccination to aged mice
Abstract
Background: The tuberculosis (TB) still increases in the number of new cases, which is estimated to approach 10 million in 2010. The number of aged people has been growing all over the world. Ageing is one of risk factors in tuberculosis because of decreased immune responses in aged people. Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette Guérin (BCG) is a sole vaccine currently used for TB, however, the efficacy of BCG in adults is still a matter of debate. Emerging the multidrug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MDR-TB) make us to see the importance of vaccination against TB in new light. In this study, we evaluated the efficacy of BCG vaccination in aged mice.
Results: The Th1 responses, interferon-γ production and interleukin 2, in BCG inoculated aged mice (24-month-old) were comparable to those of young mice (4- to 6-week-old). The protection activity of BCG in aged mice against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv was also the same as young mice.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that vaccination in aged generation is still effective for protection against tuberculosis.
Figures

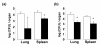
References
-
- World Health Organization. World Health Prospect. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland; 2008. http://esa.un.org/unpp/
-
- World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis control-surveillance, planning, financing. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland; 2008.
-
- Brandt L, Feino CJ, Weinreich OA, Chilima B, Hirsch P, Appelberg R, Andersen P. Failure of Mycobacterium bovis BCG vaccine: some species of environmental mycobacteria block multiplication of BCG and induction of protective immunity to tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 2002;70:672–678. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.2.672-678.2002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

