Penta-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose induces G1 arrest and DNA replicative S-phase arrest independently of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B and P53 in human breast cancer cells and is orally active against triple negative xenograft growth
- PMID: 20809980
- PMCID: PMC3096953
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr2634
Penta-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose induces G1 arrest and DNA replicative S-phase arrest independently of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B and P53 in human breast cancer cells and is orally active against triple negative xenograft growth
Abstract
Introduction: Natural herbal compounds with novel actions different from existing breast cancer (BCa) treatment modalities are attractive for improving therapeutic efficacy and safety. We have recently shown that penta-1,2,3,4,6-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose (PGG) induced S-phase arrest in prostate cancer (PCa) cells through inhibiting DNA replicative synthesis and G(1) arrest, in addition to inducing cell death at higher levels of exposure. We and others have shown that PGG through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection exerts a strong in vivo growth suppression of human PCa xenograft models in athymic nude mice. This study aims to test the hypothesis that the novel targeting actions of PGG are applicable to BCa cells, especially those lacking proven druggable targets.
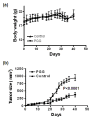
Methods: Mono-layer cell culture models of p53-wild type estrogen receptor (ER)-dependent MCF-7 BCa cells and p53-mutant ER-/progesterone receptor (PR)- and Her2-regular (triple-negative) MDA-MB-231 BCa were exposed to PGG for a comprehensive investigation of cellular consequences and molecular targets/mediators. To test the in vivo efficacy, female athymic mice inoculated with MDA-MB-231 xenograft were treated with 20mg PGG/kg body weight by daily gavage starting 4 days after cancer cell inoculation.
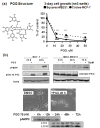
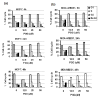
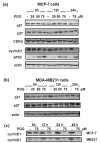
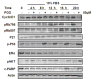
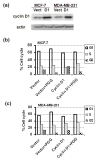
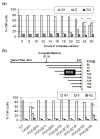
Results: Exposure to PGG induced S-phase arrest in both cell lines as indicated by the lack of 5-bromo2'-deoxy-uridine (BrdU) incorporation into S-phase cells as well as G(1) arrest. Higher levels of PGG induced more caspase-mediated apoptosis in MCF-7, in strong association with induction of P53 Ser(15) phosphorylation, than in MDA-MB-231 cells. The cell cycle arrests were achieved without an induction of cyclin dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitory proteins P21(Cip1) and P27(Kip1). PGG treatment led to decreased cyclin D1 in both cell lines and over-expressing cyclin D1 attenuated G(1) arrest and hastened S arrest. In serum-starvation synchronized MCF-7 cells, down-regulation of cyclin D1 was associated with de-phosphorylation of retinoblastoma (Rb) protein by PGG shortly before G(1)-S transition. In vivo, oral administration of PGG led to a greater than 60% inhibition of MDA-MB231 xenograft growth without adverse effect on host body weight.
Conclusions: Our in vitro and in vivo data support PGG as a potential drug candidate for breast cancer with novel targeting actions, especially for a triple negative BCa xenograft model.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Penta-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose induces S- and G(1)-cell cycle arrests in prostate cancer cells targeting DNA replication and cyclin D1.Carcinogenesis. 2009 May;30(5):818-23. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp059. Epub 2009 Mar 6. Carcinogenesis. 2009. PMID: 19269999 Free PMC article.
-
Oral administration of penta-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose suppresses triple-negative breast cancer xenograft growth and metastasis in strong association with JAK1-STAT3 inhibition.Carcinogenesis. 2011 Jun;32(6):804-11. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgr015. Epub 2011 Feb 2. Carcinogenesis. 2011. PMID: 21289371 Free PMC article.
-
Penta-1,2,3,4,6-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose induces p53 and inhibits STAT3 in prostate cancer cells in vitro and suppresses prostate xenograft tumor growth in vivo.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Sep;7(9):2681-91. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0456. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 18790750
-
Anti-cancer, anti-diabetic and other pharmacologic and biological activities of penta-galloyl-glucose.Pharm Res. 2009 Sep;26(9):2066-80. doi: 10.1007/s11095-009-9932-0. Epub 2009 Jul 2. Pharm Res. 2009. PMID: 19575286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological and biomedical functions of Penta-O-galloyl-D-glucose and its derivatives.J Nat Med. 2014 Jul;68(3):465-72. doi: 10.1007/s11418-014-0823-2. Epub 2014 Feb 15. J Nat Med. 2014. PMID: 24532420 Review.
Cited by
-
1,2,3,4,6-Penta-O-galloylglucose within Galla Chinensis Inhibits Human LDH-A and Attenuates Cell Proliferation in MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:276946. doi: 10.1155/2015/276946. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 25918543 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer Properties of Phyllanthus emblica (Indian Gooseberry).Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:950890. doi: 10.1155/2015/950890. Epub 2015 Jun 9. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 26180601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
1,2,3,4,6-penta-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose protects PC12 Cells from MPP(+)-mediated cell death by inducing heme oxygenase-1 in an ERK- and Akt-dependent manner.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2012 Oct;32(5):737-745. doi: 10.1007/s11596-012-1027-1. Epub 2012 Oct 18. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 23073806
-
Spontaneous γH2AX Foci in Human Solid Tumor-Derived Cell Lines in Relation to p21WAF1 and WIP1 Expression.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 May 20;16(5):11609-28. doi: 10.3390/ijms160511609. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26006237 Free PMC article.
-
The synthesis and antitumor activity of twelve galloyl glucosides.Molecules. 2015 Jan 27;20(2):2034-60. doi: 10.3390/molecules20022034. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 25633333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer Statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010. in press . - PubMed
-
- Chen WJ, Chang CY, Lin JK. Induction of G1 phase arrest in MCF human breast cancer cells by pentagalloylglucose through the down-regulation of CDK4 and CDK2 activities and up-regulation of the CDK inhibitors p27(Kip) and p21(Cip) Biochem Pharmacol. 2003;65:1777–1785. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

