A genetic screen identifies the Triple T complex required for DNA damage signaling and ATM and ATR stability
- PMID: 20810650
- PMCID: PMC2932975
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1934210
A genetic screen identifies the Triple T complex required for DNA damage signaling and ATM and ATR stability
Abstract
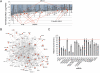
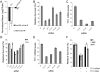
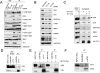
In response to DNA damage, cells activate a complex signal transduction network called the DNA damage response (DDR). To enhance our current understanding of the DDR network, we performed a genome-wide RNAi screen to identify genes required for resistance to ionizing radiation (IR). Along with a number of known DDR genes, we discovered a large set of novel genes whose depletion leads to cellular sensitivity to IR. Here we describe TTI1 (Tel two-interacting protein 1) and TTI2 as highly conserved regulators of the DDR in mammals. TTI1 and TTI2 protect cells from spontaneous DNA damage, and are required for the establishment of the intra-S and G2/M checkpoints. TTI1 and TTI2 exist in multiple complexes, including a 2-MDa complex with TEL2 (telomere maintenance 2), called the Triple T complex, and phosphoinositide-3-kinase-related protein kinases (PIKKs) such as ataxia telangiectasia-mutated (ATM). The components of the TTT complex are mutually dependent on each other, and act as critical regulators of PIKK abundance and checkpoint signaling.
Figures

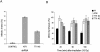


References
-
- Ahmed S, Alpi A, Hengartner MO, Gartner A 2001. C. elegans RAD-5/CLK-2 defines a new DNA damage checkpoint protein. Curr Biol 11: 1934–1944 - PubMed
-
- Benard C, McCright B, Zhang Y, Felkai S, Lakowski B, Hekimi S 2001. The C. elegans maternal-effect gene clk-2 is essential for embryonic development, encodes a protein homologous to yeast Tel2p and affects telomere length. Development 128: 4045–4055 - PubMed
-
- Collis SJ, Barber LJ, Clark AJ, Martin JS, Ward JD, Boulton SJ 2007. HCLK2 is essential for the mammalian S-phase checkpoint and impacts on Chk1 stability. Nat Cell Biol 9: 391–401 - PubMed
-
- Collis SJ, Ciccia A, Deans AJ, Horejsi Z, Martin JS, Maslen SL, Skehel JM, Elledge SJ, West SC, Boulton SJ 2008. FANCM and FAAP24 function in ATR-mediated checkpoint signaling independently of the Fanconi anemia core complex. Mol Cell 32: 313–324 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
