Introductory life science mathematics and quantitative neuroscience courses
- PMID: 20810971
- PMCID: PMC2931686
- DOI: 10.1187/cbe.10-03-0026
Introductory life science mathematics and quantitative neuroscience courses
Abstract
We describe two sets of courses designed to enhance the mathematical, statistical, and computational training of life science undergraduates at Emory College. The first course is an introductory sequence in differential and integral calculus, modeling with differential equations, probability, and inferential statistics. The second is an upper-division course in computational neuroscience. We provide a description of each course, detailed syllabi, examples of content, and a brief discussion of the main issues encountered in developing and offering the courses.
Figures


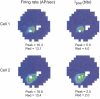
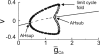
References
-
- Adler F. R. 1st ed. Belmont CA: Thomson-Brooks/Cole; 1989. Modeling the Dynamics of Life: Calculus and Probability for Life Scientists.
-
- Adler F. R. 2nd ed. Belmont CA: Thomson-Brooks/Cole, Belmont CA; 2005. Modeling the Dynamics of Life: Calculus and Probability for Life Scientists.
-
- Allman E., J. Rhodes J. Mathematical Models in Biology. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press; 2004.
-
- Bittinger M. L., Brand N., Quintanilla J. Calculus for the Life Sciences. Boston, MA: Pearson-Addison Wesley; 2006.
-
- Cullen M. R. Mathematics for the Biosciences. Fairfax, VA: Techbooks; 1983.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

